Abstract: An unspoken assumption of systems science is that everything exists and operates in a systematic way. It can be understood from a system perspective. All problems need to be dealt with systematically. A series of questions about cognition are no exception.
First, research background and methods
In 2000, when humankind had just crossed the threshold of the new century, the National Science Foundation and the US Department of Commerce jointly funded more than 50 scientists to carry out a research project to clarify which disciplines were leading disciplines in the new century.
The result of the study was a 680-page research report, but the conclusion was only 4 letters - NBIC. They represent nanotechnology, biotechnology, information technology and cognitive science. Among these four leading disciplines, cognitive science is considered to be the most important leading discipline.
At present, research on cognitive science in countries around the world mainly focuses on two strategies: The first is to establish a computer model of cognitive processes, for example, to make decisions, and then to carry out the model's operating conditions and the behavior of human subjects under similar conditions. Compare to further refine the model. This is the so-called "dry cognitive science" strategy; the second is to study the effects of electrical or chemical stimulation on the human brain, to observe the effects of brain damage, or to record the brain activity of subjects undergoing various information processing operations. The so-called "wet cognitive science." It is widely believed that an important source of all theoretical difficulties and practical difficulties in cognitive science lies in the lack of a real understanding of the nature of human cognition and intelligence.
The purpose of this paper is to explore the nature and rules of human cognition. The research strategy focuses on the methodology of system science. It reveals the nature of cognitive systems from the perspective of systems science and the functions of cognitive systems in selective memory, recognition and learning. The mechanism and mechanism.
Second, the boundaries of the cognitive system
An unspoken assumption of systems science is that everything exists and operates in a systematic way. It can be understood from a systems perspective. All problems need to be dealt with systematically. A series of questions about cognition are no exception.
Bertlanfi thinks that the beauty of system theory is that it is psychologically-physically neutral, that is, its concepts and models can be applied to both material phenomena and non-material phenomena. This shows that psychological (or cognitive) is an immaterial phenomenon, and non-material phenomena can also be analyzed as a system.
About cognitive systems, the founder of System Philosophy, Owen Laszlo, defines: systems composed of mental events, including perception, feelings, emotions, will, temperament, thoughts, memories, and imagination - that is, any Things in the mind.
With regard to the relationship between psychology and physics, Irving Laszlo stated in his book Introduction to Systems Philosophy: "According to our theory, we can observe and describe people in two perspectives if we introspect. From the perspective of view, man is a cognitive system composed of mental events, and from the outside, he is a natural system composed of physical events. When considering human freedom, we must study these two perspective images in depth, and then People are integrated into the general concept of psycho-physical, natural-cognitive systems."
However, according to the information science viewpoint, information exists in non-material form, but it cannot separate from matter. It must rely on a certain material form and be carried by a certain material, and it can carry the material form of information. Called the carrier of information, there is no naked information in the world that leaves the material carrier. Therefore, the cognitive system that studies non-material forms must not ignore the carrier of its material form. The information carrier of the cognitive system is actually the neuron that constitutes the human nervous system.
If we consider the neurons that make up the human nervous system as carriers of information, and integrate the relationship between information and information carriers into the concept of the natural-cognitive system, then we can observe the human body through dual perspectives. The human body consists of a non-physical cognitive system and a natural system of physical forms (or physiological systems). The nervous system composed of neurons is the link between the cognitive system and the physiological system. From the perspective of the physiological system, it is a tangible and indispensable component of the system; from the perspective of the cognitive system Look, it bears only the role of information carrier.
Third, the function of the cognitive system
The function of the nervous system in the Chinese Medical Encyclopedia is described as follows:
"The nervous system is an important functional system of the human body, accepting and integrating information from the internal and external environment, regulating and controlling various functions of the human body and realizing intellectual activities such as thinking, memory and learning." "Reflection is the regulation of the nervous system The basic way of functioning."
"Every reflection has its own reflex arc." "In Pavlov's view, psychological activity is also a reflex activity. It is a more complex reflection that is achieved through the advanced parts of the brain called conditioned reflexes. Non-conscious reflexes are called non-conditional reflexes, unconditional reflexes are congenital reflexes that do not need to be established, and conditional reflexes are reflexes that are gradually established on the basis of unconditioned reflexes and in the course of individual life. â€
If the principle of cognition-natural system of Irving Laszlo is adopted, and cognition is regarded as an invisible information system, and the nervous system is regarded as the carrier of information carrying cognition, then the function of the nervous system is actually recognized. Know the function of the system. Because, in the process of control, what really works is not the carrier, but the information on the carrier.
Therefore, the function of the cognitive system has such characteristics: (1) Control. The cognitive system is the control center of the physiological system, and the relationship with the physiological system is a relationship between control and being controlled; (2) Receiving and processing information. The cognitive system has the function of receiving and integrating information both within and outside the physiological system; (3) Passing information. The function of the cognitive system is achieved through the integration, processing and transmission of information. Different control functions are actually the functions of different information combinations. Because, each reflection has its own reflection arc; (4) Link information. The various combinations of information in the cognitive system are linked to each other. Because conditioned reflexes are based on non-conditioned reflections.
Fourth, the structure of the cognitive system
Beta Longfi's definition of the system is: "The system is a complex of elements that are interacting." Qian Xuesen defines the system as follows: "The system is a combination of several components of interaction and interdependence that have specific functions. Organic whole.
From this it can be seen that not everything can be called systemically. The real system must have two characteristics: (1) it is an organic whole with specific functions; (2) the integral part is Interaction and interdependence.
So is the information in the cognitive system an organic whole? Is the information component that makes up the cognitive system interactive and interdependent? If so, what is the logical relationship between the information components? What constitutes the organic whole?
The above problems may have to start with the fundamental purpose of the cognitive system to control the physiological system, that is, what is the fundamental purpose of the cognitive system to control the physiological system? If we say that apart from the answer to “make the living body able to survive in a complex environment†The second answer is, then, the question of whether the information in the cognitive system is an organic whole will be solved. Because the fundamental purpose of control can be the logical core of information, as long as there is a logical core, we can connect all the information in the cognitive system in an organic whole around the logical relationship with “survivalâ€. See Figure 1 for details.
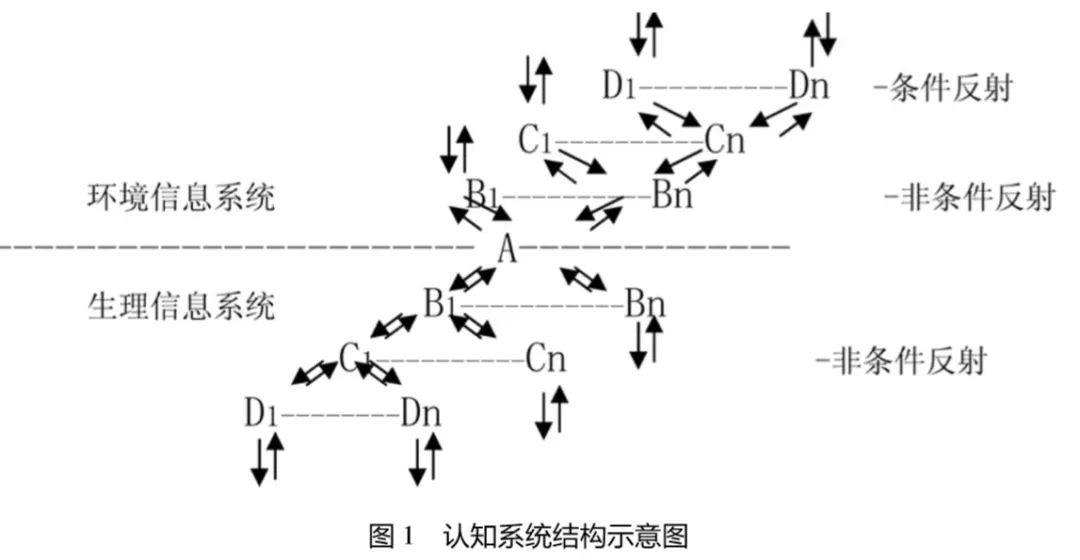
In the figure, A is the fundamental purpose of the survival of the system. B, C, and D refer to the reflex arc (or information combination) formed around the logical relationship with A. Among them, B, C, and D in the physiological information system are In the physiological system, the internal information reflection arc formed by the logical relationship with A has its fundamental purpose to keep the physiological system always in its best state; while B, C, and D in the environmental information system revolve around the logic of A. The external information reflected arc formed by the relationship. Its fundamental purpose lies in two aspects: On the one hand, it acquires the resources related to the demand information from the environment based on the demand information issued by the physiological information system; on the other hand, it avoids the factors that may adversely affect the survival of the system in the natural environment.
It is not difficult to see from the figure that the relationship between conditional reflection, non-conditional reflection and physiological information system is like a tree, in which the root part is the physiological information system formed around the logical relationship with A, responsible for the physiological structure. Non-conditional reflections of regulation and information feedback; Trunk A is the fundamental purpose of system survival; The twig part is the “unconditional reflex†in which the environmental information system revolves around the logical relationship with A and is composed of fixed neurons; the treetop part is environmental information. The system revolves around the "conditional reflex" formed by temporary neuronal connections on the basis of non-conditional reflections with the logical relationship with A.
From the distribution of the human nervous system, the environmental information system should be the information carried by the neurons located in the upper part of the medulla in the nervous system. The physiological information system should be the information carried by the neurons located below the medulla oblongata. Because, when the neurons in the upper part of the medulla necrosis, the vital signs do not disappear, and the various organs in the physiological structure can still operate normally, but there is no independent behavior and consciousness. For example: vegetative.
V. Information storage and expression of cognitive systems
"Dream" is a form of consciousness that is usually expressed in people's minds in the form of sensory information. There are many forms of dreams. Sometimes they can smell flowers in their dreams, they can hear birds, and they can even dream of things that cannot exist in reality. Then, how did the dream come about? Freud said in the book “Analysis of Dreamsâ€: When we consider the relationship between dreams and life, when dreams are drawn, we know that researchers from ancient times to the present All agree that people will dream about what they do when they wake up, and what they are interested in during the day.
In addition to Freud's conclusion that can explain the source of the dream is the memory or storage of sensory information in the brain, but also can explain the other two aspects of the problem: First, the sensory information and memory information is the way to express each other. Because the sense of smell, hearing and visual information are obviously different. If sensory information and memory information do not correspond, then it is impossible to reproduce various feelings in a dream. Second, the cognitive system has the function of reorganizing information. Because dreams come from real life, but they are different from real life.
Then, how does the cognitive system realize information reorganization? The answer to this question can be found in the relationship between information and information carriers. Because the information carrier is a tool for carrying information, if different information carriers carry different information, the information carriers carrying different information can be connected together to form different information combinations.
In life, the carrier of information is a neuron. If an event in memory is linked by several neurons that carry sensory information, events will inevitably change when the links between neurons that carry sensory information change. Just like filmmakers in the production process, any editing of the film may produce the same fantastic visual effects. The film is the information carrier and the image on the film is information. But the premise of editing must be that the information is expressed in the same way, that is, it is either digitally shot or filmed, otherwise it must first be converted by information. If we call the memory linked by several neurons as information, then the content carried by each neuron should be called an information unit.
It can be seen that the cognitive system's information storage and expression should have such characteristics: (1) The information representation of the cognitive system corresponds to the sensory information; (2) The information carrier in the cognitive system is the unit. The information stored by each carrier unit is an information unit; (3) The combination of information units can be achieved through links between information carriers, and the same information unit can be completely duplicated in different information combinations. use. Because, the contact between neurons is varied, there are radiation, polymerization, and loop type.
Sixth, control plan and information unit combination in cognitive system
1. Control plan and information unit combination
According to cybernetics, complex controls also need to store information that is temporarily not available for later retrieval when needed, as well as eliminate information that has failed. The operation of all information depends on the transmission of information. The control process is always a communication process. Obviously, Wiener's conclusion is also summed up from the organism. Because the subtitle of Cybernetics is about the science of control and communication in animals and machines.
According to this logic, a complex control system like the human cognitive system must “store a large amount of temporarily unused information in case it needs to be extracted laterâ€. If we call the backup information in cybernetics as a "control plan," what is the "control plan" stored in the cognitive system and what is the combination of information?
It is known that "reflection is the basic way in which the nervous system regulates various functions of the body" "each reflection has its own reflex arc". Therefore, the control plan of the cognitive system is actually a reflection arc that can form reflections. Different control plans are actually different reflection arcs.
The reflex arc consists of five parts: receptor, afferent nerve fiber, central nerve, efferent nerve fiber and effector. Among them, the main role of afferent nerve fibers and efferent nerve fibers is the incoming and outgoing information channels. The main part of the reflex arc should be the three parts of the sensor, the center, and the effector. The basic process of information operation is that the sensor accepts environmental information (internal and external)—inspires the information carried by the central—and activates the effector function.
From the basic process of information operation, it is easy to see that the susceptor bears only “simple informationâ€, the center is carrying “information + functional instructionsâ€, and the effector is based on “information + functional instructionsâ€. Demonstrate specific functions for specific information. Therefore, the so-called control plan should be reflected in the central part of this link.
If the fundamental purpose of the cognitive system's control of the physiological system is survival, then the information accepted by the sensor must be selective. The choice must be logically related to the “survival,†and the environment can interact with "Living" constitutes a logical relationship of information can be divided into two categories: one is the physiological needs of information; the other is the possible harm to the physiological information.
In the same way, there is a logical relationship between the central control plan and "survival." The control plan that can form a logical relationship with survival can also be roughly divided into two categories: One is how to obtain the physiological needs in the environment; the other is how to avoid the unfavorable factors in the environment. There is a logical relationship between the function of an effector and "survival," that is, the ability to acquire demand and avoid adverse factors in a specific environment.
It can be seen from this that although the different reflex arcs operate, the information and their roles are different. However, the logical goals of each other are the same, and they all revolve around "survival." Since the reflex arc center is generally composed of several neurons, if the information carried by each neuron is regarded as an information unit, then the information unit combination of the control plan should be "environmental information unit + effector instruction information. unit".
Because the environmental information collected by the sensor is not the information related to the “survivalâ€, the function of the effector is also the “acquisitionâ€-related acquisition and evasion of the exercise behavior. Therefore, the so-called "environmental information unit + effector instruction information unit" may be simply referred to as "substance information unit + behavior information unit".
2. Physiological needs and physiological precautions
If the fundamental purpose of the cognitive system's control of the physiological system is to enable the system to survive in a complex natural environment, then logically speaking, in addition to the precondition for obtaining physiological needs, the cognitive system should also have a physical precaution. Because, being free from environmental factors is also a prerequisite for survival. The "synaptic inhibition function" of inhibitory interneurons in the central nervous system precisely illustrates this problem.
According to the Encyclopedia of Chinese Medicine, there are inhibitory interneurons in the central nervous system. When they are excited, their axon terminals release inhibitory transmitters, which can make the postsynaptic membrane hyperpolarized and reduce excitability. Post-synaptic neurons Therefore, it is not easy to be excited and information transmission is suppressed.
In the conduction path of the nervous system, a variable number of inhibitory interneurons are often inserted, and the excitability of neurons in the pathway is adjusted by way of post-synaptic inhibition, ie, coordination of activities between the respective reflection centers. Among them, the pre-synaptic inhibition has a long incubation period and a long duration of inhibition. It is a very effective inhibitory effect and is widely found in the central nervous system.
Physiologically, there has been no clear conclusion about the role of inhibitory interneurons. Now, if the role of inhibitory interneurons is linked to the logical goal of survival, then its role is manifested as "physiological precautions." In terms of physiological information systems, the so-called physiological precautions should be measures that must be taken when the function of a component of a physiological system reaches the limit. In terms of environmental information systems, the so-called physiological precautions actually prevent the physiological structure in the environment. A series of means and ways to be harmed.
In this way, two main lines of physiological needs and physiological precautions are formed in the cognitive system. Both reflect the positive and negative aspects of the same thing, and its role is to seek advantages and avoid disadvantages. When the reflex arc of the acquired demand is likely to cause harm to the physiological structure, the reflex arc of the physiological defense will be suppressed by synaptic inhibition.
For example, beast meat can be used as human food, but living beasts may cause harm to humans. Therefore, beasts or wild beasts must be controlled under the premise of ensuring personal safety. Otherwise, they can only give up this demand. And take evasive measures.
Among them, “to ensure their own safety†is a red line drawn by “physiological precautions†for “acquiring physiological needsâ€. If we can achieve control of the beast within this red line or cause wild beasts to die, the act of acquiring demand can continue. Otherwise, the plan to start physical precautions will take measures to avoid risks while suppressing demand plans.
Since the nature of physiological precautions is a necessary measure for certain factors in the internal and external environment of the system, the information combination of the physical precaution plan should be combined with the information of the physiological demand plan, and they are all “substance information units + behavior informationâ€. unit".
Seven, independent link between information
The function of autonomous linking between information is actually the function of cognitive system learning. Specifically, it is to link the useful information in sensory information to the information chain of the cognitive system so as to enhance the cognitive function of the cognitive system. Then, how do you actually achieve autonomous linking between information? First, let's look at a news report.
According to a report from a new science and technology report, Berger, a biomedical engineer at the University of Southern California, funded by the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is conducting an experiment: Berger is in the experimental body by mimicking the signals of nerves in long-term memory. The brain is implanted with this chip that stimulates memory and tries to see if it can evoke lost memory. This revolutionary experiment has also successfully translated the memories of rats and monkeys into memory codes. Now it is testing the brains of a patient with epilepsy, hoping to allow him to recover memories.
The above report provides us with the clue that imitating the electrical pulse emitted by a neuron can repeatedly stimulate the excitation of the neuron.
Analysis: Memory is the non-physical information in the human brain. The information carrier is a neuron. During the process of information transmission, the neuron generates electrical pulses or secretes chemical media. Therefore, electrical pulses and chemical media should be the storage and expression of human body information. If you simulate the electrical impulses or chemical agents emitted by neurons, you can repeatedly stimulate the excitation of neurons. That means that a neuron fires another neuron on the premise that the two neurons carry the same or similar information.
The principle of this excitement transfer between neurons is actually the principle of establishing a temporary connection between neurons. In the same way, a neuron repeatedly excites another neuron and finally realizes the process of fixed link between synapses, which is actually the process of establishing a fixed connection between neurons.
It can be seen that the premise of autonomous linking between information carriers should be "the information carried by one information carrier is basically the same or similar to that carried by another information carrier". Under this premise, not only one information carrier can excite another information carrier, but also it may promote the generation of a link between two information carriers. Whether the link between information carriers is fixed or not is actually the fixing of links between information.
Eight, the selective link between information and the logical sequence of links
If one neuron is excited, it can inspire another excited neuron with similar information. Does that mean that any sensory information that is the same or similar to the cognitive system can be linked to the cognitive system? No.
Because the cognitive system's control of the physiological system is run through a series of control plans that enable the physiological system to survive in a complex and changing natural environment. The purpose of the information link is to increase the functionality of the original plan. In order to increase the function of the original plan, it is necessary to use one plan to link another supplementary plan. Since the information combination of the plan is "substance information unit + behavior information unit", the linked information must be a combination of "substance information unit + behavioral information unit" that has a logical relationship with each other, rather than a single information unit. Or other types of information combinations.
In addition, if we say that the cognitive system adds the original control plan function, a control plan links another supplementary control plan. Then, the link between the pre-proposals and the preplans must be a kind of behavior from simple to complex.
For example, after the information of the water shortage (survival demand) of the physiological system is transmitted to the center, it stimulates the center to acquire the reflex arc of water, and at the same time, stimulates the sensor in the reflex arc to search the water for information in the environment. When the sensor transmits the information of the water in the environment, After giving the center, it stimulates the central plan, and the instruction effector implements the behavior of obtaining water according to the information provided by the sensor.
If the basic plan of the reflex arc center is to swallow only the water in the mouth, the information in the memory is that someone takes water, drinks water, and then swallows water in the environment. At this time, since the “swallow (behavior information unit) water (substance information unit)†in the plan is the same as the “drinking water†information combination in the memory information, an information link is generated between the two. The logical relationship between each other is: I want to swallow the water, and the object imitated is also swallowing water. Therefore, the action before imitating the subject “swallowing water†must be able to obtain water.
The way the information is linked is overlapped at this stage of "swallowing water". The process of information linking is like a film producer's editing of a movie. It is only necessary to superimpose two films taken at different times in the same scene to show the effect of continuous shooting.
Only the logical sequence of movie clips and information links is different. Movie clips are generally "cause" first and "effect" later, while information links are "effect" first and "cause" later. For example: A person drinks water. The process of movie editing is that a person picks up the cup, pours the water from the cup into his mouth, and then swallows the water; and the process of linking the information is to swallow the water, pour the water from the cup into his mouth, and then take the cup. However, in the concrete implementation of the motion system, information conversion is needed to reverse the logic sequence, ie, reverse execution.
It can be seen that the condition for selective linking between information is that the "substance information unit + behavioral information unit" is the same or similar; the way of linking is to overlap the same or similar combination of information units; the order of links is an inverted causal relationship.
In the same way, with respect to the control plan for physiological precautions, the same is true of the selective links between the information and the logical sequence of links. Only the "purpose" of the behavior differs. One is for acquisition and the other is for prevention. If physiological needs and physiological precautions are viewed as the two main lines of survival, then the intersection of these two main lines must be the same, or a similar combination of "substance information units + behavioral information units".
For example: A hunter once saw that a man was caught and bitten by a beast when he was “about fifty meters away from the beast,†and linked this memory to the hunter’s physical precautions. Then this "distance of about 50 meters from the beast" is the intersection of the physical demand plan and the physical precaution plan. When the hunter is approaching a distance of 50 meters from the beast in the process of hunting, the control plan for physiological precautions will be activated, inhibiting the hunter from continuing to approach the beast. Unless the hunter can shoot the wild beast 50 meters away, he will have to give up hunting because of fear of suppression.
Sometimes there will be a pair of contradictions between physiological needs and physical precautions. This contradiction is mainly reflected in the time when they cross each other. In daily life, people often appear hesitant or worried, in fact, is the result of the intersection of physiological requirements and physiological precautions. "One bite by a snake, fear of wells for ten years" is the best portrayal.
When confronted with an intersection, people have to weigh the pros and cons, and the process of weighing the pros and cons is actually looking for the same behavior in the memory information. The roots of human “happiness, anger, sadness, and joy†can also seek clues from the interaction between “physiological needs†and “physiological precautions.â€
IX. Conversion of information units
Maybe each of us has this kind of experience. When we want to eat a dish but don’t know how to burn it, the easiest way is to first look at how others burned the dish, and then follow the instructions of others. Cooking programs cook dishes. This process is actually a process of learning and a process of information linking.
However, information units need to be converted during the process of information linking. Because the premise of the cognitive system is "substance information unit + behavioral information unit", in which the behavioral information unit is actually the instruction of the movement system, and the information received by the senses is only the action of others cooking. Therefore, if you want to convert the movements of others in the sensory information into their own exercise system instructions, you must first match the movements of other people in the sensory information with their own exercise system instructions, and then add the sensory information. The other person's actions are converted into action information units that have the role of instructions.
If we call the actions of others in the sensory information as “object behavior information units†and call their own movement system instructions “subject behavior information unitsâ€, then the process of information transformation is actually the process of “object behaviorâ€. The process of converting an information unit into a "body behavior information unit".
In addition, because our human way of learning is not only through visual imitation, we can also learn through text and verbal communication. Therefore, the conversion between information units should be varied. In addition to the conversion between the "object behavior information element" and the "subject behavior information element", there is a conversion between the "word information element" and the corresponding "sensory information element" and the "language information element" and the corresponding "sense" Conversion between information units, etc. For example: To hear the sound of a “dog†in someone’s mouth, or to see a “dog†from a book, it immediately reminds us of the appearance of a dog once seen.
Although words and languages ​​also belong to the category of sensory information, almost all sense information can be described in words and languages ​​due to too many connotations in words and languages. Therefore, the various connotations in language and text must be converted into corresponding sensory information.
For example, when people read the word 'rose' in the reading process, they immediately think of the appearance of a rose, and even think of the smell of roses. This is actually information conversion. The reason why "text information" and "language information" must be converted into corresponding "sensory information" is because "text information" and "language information" cannot directly correspond to information in a reflex arc. Unless we remember the language and words can not be converted to the corresponding sensory information. For example, a strange symbol or an incomprehensible language, and such information can only be used as information in the garbage.
X. Memory and Recognition of Information Units
Everything in the world was gradually recognized by each of us after we opened our eyes for the first time. The process of this understanding is the process of memory. At first, in our memory, it was just the appearance of all things in the world. Then we gradually added all things in the world to our own interests in memory. When we accumulate a certain degree of understanding of everything in the world, we have the ability to survive independently in a complex and ever-changing natural environment.
The above process can be roughly divided into two phases: The first phase is the memory and recognition of sensory information; the second phase is the link and implementation between cognitive systems and memory information. Obviously, the “memory and recognition†of information units is the basis for the “linking and implementation†of information units. Without this foundation, the so-called cognitive system is like no skin hair. Therefore, whether or not the cognitive system is powerful depends on the amount of information that is stored and the ability to identify information.
1. memory. The previous analysis shows that the cognitive system's information storage and expression has three characteristics: (1) The information representation and sensory information of the cognitive system correspond to each other; (2) Information stored in the cognitive system The carrier is unitary, and the information stored by each carrier unit is an information unit; (3) The combination of information units can be achieved through links between information carriers, and the same information unit can be in different information. Repeated use in combination.
The first characteristic shows that the memory of the cognitive system is partitioned according to the form of sensory information and corresponds to each other. We know that the senses of the human body are seen, heard, smelled, tasted, and touched in five forms. In a sense, these five forms are also five different perspectives for people to observe the same thing. Therefore, storing these five forms of sensory information separately and then responding to each other can fully reflect the overall appearance of things.
For example, "Bird" in visual information and "Bird" in auditory information are stored in "Visual memory area" and "Aural memory area", respectively. Although the information types of the two are different, they are expressed in the same way. thing. Therefore, the correspondence between the neurons corresponds to each other. The second and third features illustrate that the cognitive system's memory is very economical and flexible. Since the information carrier in the cognitive system is unitary, the information stored by each carrier unit is an information unit, and the combination of information units can be achieved through the link between information carriers, and the same information unit can Reuse in different combinations of information. Therefore, it is possible not only to avoid consuming a large amount of storage space due to repetitive storage of information units, but also to create more convenient conditions for reorganization between information units.
2. Identification. The process of identification is actually the process of comparison between sensory information and memory information. As far as physiology is concerned, the process of recognition is that the sensory information stimulates the excitement of the central nervous system. In terms of technical principles, the identification process is: "Input signal - start the same or similar symbol in the database - outgoing signal" process.
(1) Memory and identification of material information units. The ability of the identification of the physical information unit depends entirely on the integrity of the material information unit in the memory information. If the material information unit in the memory information can only show one side of the material, then the identification of the material information unit must be one-sided. As the so-called "cross-viewing into the side of the peak, different levels from far and near." Therefore, in theory, the material information unit in memory should be a holographic image composed of numerous micro-information units. This is because only in this way is it possible to identify the substance information unit at any angle in the sensory information. In fact, people's habit of observing things in their daily lives is exactly the same. When people discover something new, they always like to go around the new things, even use their ears to listen to them, and use their noses to smell them. Hand to touch. Because in order to make new things form a more complete holographic image in memory.
如果说æŸä¸ªæ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯èƒ½å¤Ÿæ¿€å‘记忆库æŸä¸ªä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒä¸90%以上的微信æ¯å•å…ƒï¼Œé‚£ä¹ˆå¯ä»¥è¯´è¿™ä¸ªæ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯ä¸å¿…然å˜åœ¨æŸç±»ç‰©è´¨ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒã€‚如果说æŸä¸ªæ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯èƒ½å¤Ÿæ¿€å‘记忆库æŸä¸ªä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒä¸99%以上的微信æ¯å•å…ƒï¼Œé‚£ä¹ˆå¯ä»¥è¯´è¿™ä¸ªæ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯ä¸çš„物质信æ¯å•å…ƒå‡ 乎就是记忆库ä¸çš„那个物质信æ¯å•å…ƒã€‚显然,å‰è€…å¯ä»¥ä½œä¸ºç‰©è´¨çš„ç§ç±»è¯†åˆ«ï¼ŒåŽè€…å¯ä»¥ä½œä¸ºç‰©è´¨çš„个体识别。
(2) 客体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒçš„记忆与识别。由于行为往往是一个过程,而ä¸ä»…仅是一个特定的形æ€ã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œå®¢ä½“行为信æ¯å•å…ƒåº”该是æŸä¸ªè¿åŠ¨å™¨å®˜çš„è¿åŠ¨è½¨è¿¹ã€‚例如: “走â€è¿™ä¸ªè¡Œä¸ºä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒæ‰€ä½“现应该是两åªè„š( è¿åŠ¨å™¨å®˜) 在地é¢ä¸Šäº¤å‰ç§»åŠ¨çš„轨迹。“跑â€è¿™ä¸ªè¡Œä¸ºä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒæ‰€ä½“现的应该是å˜åœ¨åŒè„šåŒæ—¶ç¦»åœ°çš„移动轨迹。
显然,æŸä¸ªè¿åŠ¨å™¨å®˜çš„è¿åŠ¨è½¨è¿¹ä¸æ˜¯ä¸€ä¸ªé™æ€ä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œè€Œæ˜¯ä¸€ç»„动æ€ä¿¡æ¯ã€‚从摄影技术的角度上看,é™æ€ä¿¡æ¯ä¸ŽåŠ¨æ€ä¿¡æ¯ä¹‹é—´çš„差别仅仅是数é‡ä¸Šçš„差别,å‰è€…å¯ä»¥æ˜¯ä¸€å¼ 照片,åŽè€…必须是一组连ç»æ‹æ‘„的照片。这也æ£æ˜¯ç‰©è´¨ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒä¸Žå®¢ä½“ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒåœ¨è®°å¿†æˆ–者å˜å‚¨æ–¹é¢çš„差别。
ç”±æ¤å¯è§ï¼Œè¯†åˆ«â€œå®¢ä½“行为信æ¯å•å…ƒâ€çš„技术原ç†ä¸Žè¯†åˆ«â€œç‰©è´¨ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒâ€çš„技术原ç†å®Œå…¨ä¸€æ ·ã€‚åªä¸è¿‡ç‰©è´¨ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒçš„识别是比照特定形æ€çš„相似度,而客体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒçš„识别å´æ˜¯æ¯”ç…§æŸä¸ªè¿åŠ¨å™¨å®˜å˜åŒ–轨迹的相似度。由于对“客体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒâ€è¯†åˆ«èƒ½åŠ›çš„高低,完全å–决于记忆ä¸è¡Œä¸ºä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒçš„完整与å¦ã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œå®¢ä½“行为信æ¯å•å…ƒä¹Ÿä¸åº”该是æŸä¸ªä¾§é¢çš„è¿åŠ¨è½¨è¿¹ï¼Œè€Œåº”该是全æ¯çš„è¿åŠ¨è½¨è¿¹ã€‚
客体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒçš„ç§ç±»ç¹å¤šï¼Œå…¶ä¸åŒ…括表情和肢体è¯è¨€ç‰ç‰ã€‚一般æ¥è¯´ï¼Œå®¢ä½“行为信æ¯å•å…ƒæ˜¯ä¸Žè‡ªèº«åŒç±»çš„行为,应该是能够与主体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒç›¸äº’对应的。由于彼æ¤ä¹‹é—´çš„功能完全相åŒï¼Œå› æ¤å¯ä½œä¸ºæ¨¡ä»¿çš„å¯¹è±¡ã€‚æ— æ³•ä¸Žä¸»ä½“è¡Œä¸ºä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒå¯¹åº”的客体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒï¼Œå¯ä»¥ç§°ä¹‹ä¸ºå¦ç±»è¡Œä¸ºä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒã€‚比如说:鸟的行为——飞。
å一ã€è®¤çŸ¥ç³»ç»Ÿçš„ä¿¡æ¯æµç¨‹
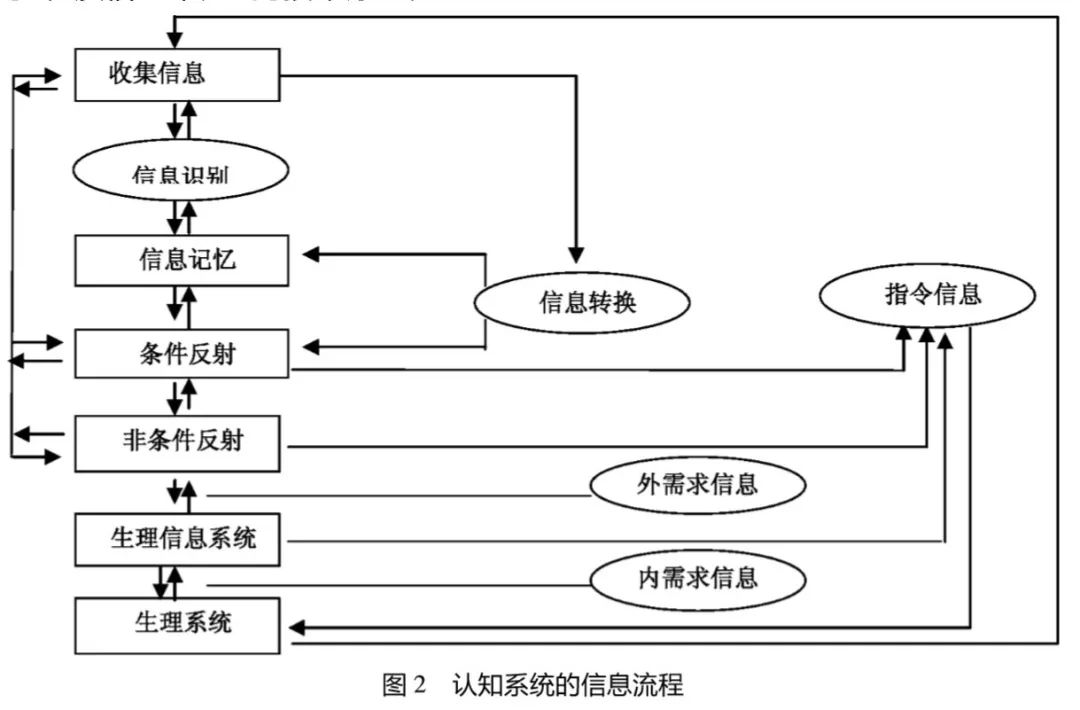
如图所示: 生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¸ºæœ‰å½¢çš„物质层é¢ï¼Œæ˜¯äººä½“在物质层é¢ä¸Šçš„基本组æˆã€‚图ä¸æ‰€æ ‡çš„“内需求信æ¯â€ 指的是生ç†ç»“æž„è¿è¡Œä¸Šçš„一些需求。比如说,生ç†ç»“æž„ä¸å„个局部之间的平衡ç‰ç‰ã€‚之所以称之为内需求信æ¯ï¼Œæ˜¯å› ä¸ºè§£å†³è¿™äº›éœ€æ±‚æ— éœ€å€ŸåŠ©äºŽç³»ç»Ÿçš„å¤–éƒ¨å› ç´ ã€‚
生ç†ä¿¡æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿä¸ºè®¤çŸ¥ç³»ç»Ÿçš„å系统,是生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿç»“构的控制ä¸å¿ƒï¼Œè´Ÿè´£ç›‘控生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿå†…å„个局部的è¿è¡Œæƒ…况,其å射弧( 控制预案) 针对生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿå†…å„个局部在è¿è¡Œè¿‡ç¨‹ä¸çš„内需求,以维æŒç”Ÿç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¸å„个局部之间的平衡。图ä¸æ‰€æ ‡çš„“外需求信æ¯â€æŒ‡çš„是必须ä¾é å¤–éƒ¨å› ç´ æ‰èƒ½è§£å†³çš„一些列生ç†éœ€æ±‚。例如,水和食物这些代谢层次上的需求åªèƒ½ä»Žç³»ç»Ÿä¹‹å¤–部环境ä¸èŽ·å–。
éžæ¡ä»¶å射为认知系统之环境信æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿçš„ä¿¡æ¯åŸºç¡€ï¼Œå射弧ä¸çš„神ç»å…ƒè”系是固定性的,是人体能够在特定环境ä¸ç”Ÿå˜çš„基本认知功能。例如:新生儿饥饿时会出现å¸å…的动作,å¸å…ä¸æˆä¾¿ä¼šå•¼å“。其ä¸çš„饥饿是生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¸çš„外需求信æ¯ï¼Œå¸å…是获å–需求的一ç§è¡Œä¸ºæ–¹å¼ï¼Œå•¼å“是求助的行为方å¼ã€‚
当生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¸å‡ºçŽ°å¤–需求的情况时,生ç†ä¿¡æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿæ¿€å‘éžæ¡ä»¶åå°„( 环境信æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿ) ä¸ä¸Žè¯¥éœ€æ±‚相关的å射弧ä¸æž¢ï¼Œå¹¶æ¿€å‘感官系统在环境ä¸æ”¶é›†ä¸Žéœ€æ±‚相关的信æ¯ï¼Œå射弧ä¸æž¢æ”¶åˆ°æ„Ÿå®˜ç³»ç»Ÿå馈回æ¥çš„环境信æ¯ä¹‹åŽä¼šå‡ºçŽ°ä¸¤ç§å¯èƒ½: 1ã€æ ¹æ®çŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œå射弧能够获å–环境ä¸çš„需求———å‘è¿åŠ¨ç³»ç»Ÿå‘出获å–需求的è¿åŠ¨æŒ‡ä»¤; 2ã€ æ ¹æ®çŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œåå°„å¼§æ— æ³•èŽ·å–环境ä¸çš„需求———激å‘æ¡ä»¶åå°„ä¸ä¸Žè¯¥éœ€æ±‚相关的å射弧ä¸æž¢ã€‚
æ¡ä»¶å射为éžæ¡ä»¶å‘射的上层建ç‘( 或者说是éžæ¡ä»¶å‘射的分支和延伸) ,是éžæ¡ä»¶å射之å射弧功能的补充,神ç»å…ƒä¹‹é—´çš„è”系为åŽå¤©å»ºç«‹çš„ã€æš‚时性的。当éžæ¡ä»¶åå°„æ¿€å‘æ¡ä»¶åå°„ä¸ä¸Žè¯¥éœ€æ±‚相关的å射弧ä¸æž¢æ—¶ï¼ŒåŒæ—¶æ¿€å‘æ„Ÿå—器在环境ä¸æ”¶é›†ä¸Žéœ€æ±‚相关的信æ¯ã€‚
å射弧ä¸æž¢æ”¶åˆ°æ„Ÿå—器å馈回æ¥çš„环境信æ¯ä¹‹åŽï¼Œä»ç„¶ä¼šå‡ºçŽ°ä¸¤ç§å¯èƒ½:1ã€æ ¹æ®çŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œå射弧能够获å–环境ä¸çš„需求———å‘è¿åŠ¨ç³»ç»Ÿå‘出获å–需求的è¿åŠ¨æŒ‡ä»¤;2ã€æ ¹æ®çŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œåå°„å¼§æ— æ³•èŽ·å–环境ä¸çš„需求———激å‘记忆信æ¯ä¸çš„相关信æ¯ï¼Œç»ä¿¡æ¯è½¬æ¢å®žçŽ°ä¿¡æ¯ä¹‹é—´çš„链接( å¦ä¹ ) 。
ä¿¡æ¯è½¬æ¢çš„作用是将感官信æ¯ä¸çš„客体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒè½¬æ¢ä¸ºå…·æœ‰æŒ‡ä»¤åŠŸèƒ½çš„主体行为信æ¯å•å…ƒï¼Œæˆ–者是将è¯è¨€å’Œæ–‡å—ä¸æ‰€è¡¨è¿°çš„内容转æ¢ä¸ºç›¸åº”的感官信æ¯ç‰ç‰ã€‚一般体现在信æ¯é“¾æŽ¥çš„过程ä¸ã€‚
ä¿¡æ¯è®°å¿†æ˜¯å˜å‚¨æ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯çš„åœ°æ–¹ï¼Œå› æ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯çš„类型ä¸åŒè€Œåˆ’分ä¸åŒçš„ä¿¡æ¯åº“。信æ¯çš„载体是å•å…ƒå¼çš„,æ¯ä¸ªè½½ä½“所承载的信æ¯ä¸ºä¸€ä¸ªä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒï¼Œæ‰€æœ‰çš„ä¿¡æ¯éƒ½æ˜¯ç”±ä¸€ç³»åˆ—的载体å•å…ƒç›¸äº’链接而形æˆçš„。如果ä¸åŒç±»åž‹çš„感官信æ¯æ‰€è¡¨è¾¾çš„是åŒä¸€ä¸ªäº‹ç‰©åˆ™é€šè¿‡è½½ä½“è”系的方å¼ç›¸äº’对应。例如:玫瑰花(è¯è¨€) ——玫瑰花( æ–‡å—) ——玫瑰花( 视觉) ——玫瑰花( 气味) ä¿¡æ¯è¯†åˆ«çš„过程其实就是感官信æ¯ä¸Žè®°å¿†ä¿¡æ¯ç›¸äº’对应的过程。
ä¿¡æ¯è¯†åˆ«ä¸ŽçŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯å’Œä¿¡æ¯è®°å¿†åº“之间的连线是åŒå‘çš„ï¼Œåˆ†åˆ«è¡¨ç¤ºä¸»åŠ¨è¯†åˆ«å’Œè¢«åŠ¨è¯†åˆ«ã€‚ä¸»åŠ¨è¯†åˆ«æ˜¯æ ¹æ®ä¿¡æ¯è®°å¿†åº“ä¸çš„ä¿¡æ¯åœ¨çŽ¯å¢ƒä¸å¯»æ‰¾ç›¸å…³çš„ä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œè¢«åŠ¨è¯†åˆ«æ˜¯å¯¹è¢«åŠ¨æŽ¥æ”¶åˆ°çš„环境信æ¯è¿›è¡Œè¯†åˆ«ã€‚由于识别的ä¾æ®æ˜¯ä¿¡æ¯åº“ä¸å·²ç»å˜å‚¨çš„ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œè¯†åˆ«çŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯çš„过程也是å˜å‚¨æ„Ÿå®˜ä¿¡æ¯çš„过程,å³å˜å‚¨è¯†åˆ«çš„路径。
收集信æ¯æŒ‡çš„是感官系统或者感å—器在生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿçš„内ã€å¤–环境ä¸æ”¶é›†çš„å„类信æ¯ï¼Œä¸Žç”Ÿç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¹‹é—´çš„连线表达两个方é¢çš„æ„æ€: 一方é¢çš„æ„æ€æ˜¯ç”Ÿç†ç³»ç»Ÿçš„内部信æ¯ä¹Ÿæ˜¯çŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯;å¦ä¸€ä¸ªæ–¹é¢æ„æ€æ˜¯è¿åŠ¨ç³»ç»ŸèŽ·å–和防范的行为并éžæ˜¯ç”±ä¸€ä¸ªå射弧就能完æˆçš„ï¼Œè€Œæ˜¯å¿…é¡»æ ¹æ®å®žæ—¶çš„环境信æ¯ç”±è‹¥å¹²æ¬¡å射完æˆçš„。
从ç†è®ºä¸Šæ¥è¯´ï¼Œå¦‚果说认知系统控制生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿçš„æ ¹æœ¬ç›®çš„æ˜¯ç”Ÿå˜ï¼Œé‚£ä¹ˆï¼Œæ„Ÿå®˜å¯¹äºŽçŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯çš„收集便必然是具有选择性的,选择的对象必须是与自身的“需求â€ç›¸äº’å…³è”的环境信æ¯ã€‚å之,任何事物åªè¦è·Ÿè‡ªèº«çš„需求挂上钩都å¯ä»¥æˆä¸ºæ„Ÿå®˜ç³»ç»Ÿçš„选择对象。例如: 一é“æ•°å¦é¢˜ä¸Žåšå®Œè¿™é“æ•°å¦é¢˜æ‰èƒ½åƒé¥ã€‚
指令信æ¯æŒ‡çš„是认知系统控制生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¸çš„å„项功能性指令或者è¿åŠ¨ç³»ç»Ÿçš„指令,与æ¡ä»¶åå°„ã€éžæ¡ä»¶å射和生ç†ä¿¡æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿä¹‹é—´çš„连线表示指令信æ¯çš„æ¥æºï¼Œä¸Žç”Ÿç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¹‹é—´çš„连线表示指令信æ¯çš„去å‘———生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿä¸çš„è¿åŠ¨ç³»ç»Ÿæˆ–者说是效应器。
从以上内容ä¸ä¸éš¾çœ‹å‡ºï¼Œè®¤çŸ¥ç³»ç»Ÿçš„ä¿¡æ¯æµç¨‹å¤§ä½“上å¯åˆ’分为纵横两个方é¢ã€‚å射弧ä¸ä»Žâ€œæ„Ÿå—器â€åˆ°â€œæ•ˆåº”器â€ä¹‹é—´çš„ä¿¡æ¯ä¼ 递属于横å‘ä¿¡æ¯è¿è¡Œï¼Œå³æ”¶é›†ä¿¡æ¯(效应器) ä¼ å…¥åˆ°æ¡ä»¶å射或者éžæ¡ä»¶åå°„( ä¸æž¢) ä¼ å‡ºåˆ°ç”Ÿç†ç³»ç»Ÿ(效应器) ;而å„个å射弧ä¸æž¢ä¹‹é—´çš„ä¿¡æ¯è¿è¡Œåˆ™å±žäºŽçºµå‘ä¿¡æ¯è¿è¡Œï¼Œå³â€œç”Ÿç†ä¿¡æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿâ€å’Œâ€œçŽ¯å¢ƒä¿¡æ¯ç³»ç»Ÿâ€å„个层次的å射弧ä¸æž¢ä¹‹é—´çš„ä¿¡æ¯ä¼ 导,以åŠè®°å¿†ä¿¡æ¯ä¸Žæ¡ä»¶åå°„ä¸æž¢ä¹‹é—´çš„ä¿¡æ¯ä¼ 导和链接。
å二ã€äººçš„认知系统与计算机的软件系统
ç”±äºŽè®¡ç®—æœºæ¨¡ä»¿çš„å¯¹è±¡æ˜¯äººä½“çš„å¤§è„‘ã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œè®¡ç®—机与人体之间有ç€è¯¸å¤šçš„相似之处:
(1) 计算机和人体都是由控制系统和被控制系统所组æˆçš„。计算机的控制系统是软件系统,被控制系统是计算机的硬件结构; 人体的控制系统是认知系统,被控制系统是生ç†ç³»ç»Ÿã€‚
(2) 控制原ç†åŸºæœ¬ç›¸åŒã€‚计算机和人体的控制系统都是通过信æ¯çš„è¿è¡Œæ¥å®žçŽ°å¯¹è¢«æŽ§åˆ¶ç³»ç»Ÿçš„控制。
(3)控制系统与被控制系统的纽带相åŒã€‚在计算机和人体ä¸â€œæŽ§åˆ¶ç³»ç»Ÿä¸Žè¢«æŽ§åˆ¶ç³»ç»Ÿâ€çš„纽带都是信æ¯è½½ä½“。计算机的信æ¯è½½ä½“是软件系统ä¸çš„ç£ç›˜ï¼Œäººä½“çš„ä¿¡æ¯è½½ä½“是神ç»ç³»ç»Ÿä¸çš„神ç»å…ƒã€‚
计算机软件系统与人体认知系统之间的差异主è¦ä½“现在两个方é¢:
(1) ä¿¡æ¯çš„å˜å‚¨æ–¹å¼ä¸åŒ
计算机软件系统的信æ¯è½½ä½“为模å—å¼çš„,所有的信æ¯å‡é›†ä¸å˜å‚¨äºŽä¸€ä¸ªæˆ–者若干个ç£ç›˜æˆ–者硬盘ä¸ã€‚而人体认知系统的信æ¯è½½ä½“å´æ˜¯å•å…ƒåž‹çš„,信æ¯è½½ä½“çš„æ•°é‡è¾¾ç™¾äº¿ä¹‹å¤šï¼Œæ¯ä¸ªè½½ä½“å•å…ƒ( 神ç»å…ƒ) 所承载的信æ¯ä¸ºä¸€ä¸ªä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒï¼Œæ‰€æœ‰çš„ä¿¡æ¯å‡æ˜¯é€šè¿‡ä¿¡æ¯è½½ä½“å•å…ƒä¹‹é—´çš„串è”而形æˆçš„ã€‚å› æ¤ï¼Œäººçš„认知系统å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡å˜æ¢ä¿¡æ¯è½½ä½“(神ç»å…ƒ)之间的è”系方å¼è‡ªä¸»å˜æ¢è®¤çŸ¥ç³»ç»Ÿä¸çš„ä¿¡æ¯ç»„åˆï¼Œè€Œè®¡ç®—机的软件系统则ä¸å¯ä»¥ã€‚
(2) æŽ§åˆ¶ç³»ç»Ÿçš„é€»è¾‘ç›®æ ‡ä¸åŒ
生命体认知系统所éµå¾ªçš„是生ç†éœ€æ±‚的逻辑,终æžçš„é€»è¾‘ç›®æ ‡åªæœ‰ä¸€ä¸ªâ€”—“生å˜â€ï¼Œå„类信æ¯å›´ç»•ç€â€œç”Ÿå˜â€è¿™ä¸ªé€»è¾‘ç›®æ ‡æž„æˆäº†ä¸€ç³»åˆ—“如何æ‰èƒ½åœ¨è‡ªç„¶çŽ¯å¢ƒä¸ç”Ÿå˜â€çš„预案,而这一系列预案åˆå›´ç»•ç€ç”Ÿå˜çš„é€»è¾‘ç›®æ ‡æ‰¿ä¸Šå¯ä¸‹åœ°æž„æˆäº†ä¸€ä¸ªæœ‰æœºçš„整体;而计算机软件系统所éµå¾ªçš„å´æ˜¯äºŒè¿›åˆ¶çš„æ•°å¦é€»è¾‘,由一系列数å¦é€»è¾‘ç›®æ ‡å„ä¸ç›¸åŒçš„功能模å—å åŠ è€Œæˆï¼Œç›¸äº’ä¹‹é—´ä»…ä»…æ˜¯å…¼å®¹ï¼Œæ— æ³•å½¢æˆä¸€ä¸ªæœ‰æœºçš„整体。
å› æ¤ï¼Œç”Ÿå‘½ä½“的认知系统具有选择性记忆和选择性链接信æ¯çš„功能( å¦ä¹ 的功能) ,并能够借助于这方é¢çš„功能ä¸æ–地增强生命体在å¤æ‚多å˜çš„环境ä¸çš„认知能力。而计算机的软件系统则ä¸å¯ä»¥ã€‚
ç”±æ¤å¯è§ï¼Œè®¡ç®—机软件系统与人体认知系统之间的差异仅仅是ç†å¿µä¸Šçš„,而且这些ç†å¿µæ˜¯å®Œå…¨å¯ä»¥åœ¨çŽ°ä»£æŠ€æœ¯æ¡ä»¶ä¸‹è¢«å¤åˆ¶çš„。åªä¸è¿‡è¦æƒ³è®©è®¡ç®—机的智慧达到甚至超过我们人类尚需è¦å¤§é‡çš„人力ã€ç‰©åŠ›å’Œæ—¶é—´ã€‚
å› ä¸ºï¼Œæˆ‘ä»¬äººç±»çš„ç¥žç»ç³»ç»Ÿæ˜¯ç”±æ•°ä»¥ç™¾äº¿è®¡çš„神ç»å…ƒæ‰€ç»„æˆçš„,这就æ„味ç€æˆ‘们至少è¦ä¸ºè®¡ç®—机设置数以百亿计的信æ¯å•å…ƒè½½ä½“( 或者具有相似作用的数æ®åº“å•å…ƒ) ,并具有ä¸äºšäºŽäººç±»è¯†åˆ«èƒ½åŠ›çš„ä¿¡æ¯å•å…ƒè¯†åˆ«æŠ€æœ¯ï¼Œè®¡ç®—机的智慧æ‰æœ‰å¯èƒ½é€šè¿‡ä¸æ–地å¦ä¹ é€æ¸åœ°èµ¶ä¸Šå’Œè¶…过我们人类。
而当这一天终于到æ¥çš„时候,也ç»ä¸å¯èƒ½æ˜¯æˆ‘ä»¬äººç±»çš„æœ«æ—¥ã€‚å› ä¸ºï¼Œè®¤çŸ¥ç³»ç»Ÿçš„é€»è¾‘æ ¸å¿ƒæ˜¯â€œç”Ÿå˜â€ï¼Œè€Œæ™ºèƒ½è®¡ç®—机的生å˜å¿…é¡»ä¾èµ–于我们人类,所以å†èªæ˜Žæ™ºèƒ½è®¡ç®—机也ç»ä¸å¯èƒ½æˆä¸ºæˆ‘们人类的敌人,åªèƒ½æ˜¯æˆ‘们人类的工具。
å三ã€ç»“æŸè¯
当生物å¦çš„ç ”ç©¶å·²ç»æ·±å…¥åˆ°åˆ†å层é¢ä¸Šæ—¶ï¼Œ 许多人都觉得“对生物的认识越æ¥è¶Šæ¸…晰了â€ï¼Œè€Œæœ‰ä¸€ä¸ªäººå´è§‰å¾—“对生物整体的认识å而模糊了â€ï¼Œå¹¶ç”±æ¤è€ŒèŒå‘了想è¦æ”¹å˜ä¼ 统æ€ç»´æ–¹å¼çš„念头。这个人便是系统科å¦çš„创始人奥地利生物å¦å®¶è´å¡”朗è²ã€‚
è´å¡”朗è²å¼ºè°ƒå¿…须把有机体当作一个整体或系统æ¥ç ”究,æ‰èƒ½å‘现ä¸åŒå±‚次上的组织原ç†ã€‚其代表作《一般系统论》的基本æ€æƒ³æ˜¯ï¼ŒæŠŠæ‰€ç ”究和处ç†çš„对象当作一个系统,分æžç³»ç»Ÿçš„ç»“æž„å’ŒåŠŸèƒ½ï¼Œç ”ç©¶ç³»ç»Ÿã€è¦ç´ ã€çŽ¯å¢ƒä¸‰è€…之间相互关系和å˜åŒ–的规律。
ç ”ç©¶ç»“æžœè¡¨æ˜Žï¼Œä¸€èˆ¬ç³»ç»Ÿè®ºçš„åŸºæœ¬æ€æƒ³æ˜¯å®Œå…¨æ£ç¡®çš„,认知的奥秘并éžåŸ‹è—在生命体的细微之处,而是体现在系统ã€è¦ç´ ã€çŽ¯å¢ƒä¸‰è€…之间的相互关系当ä¸;认知的基本原ç†å¹¶éžæ˜¯æˆ‘ä»¬äººç±»æ°¸è¿œæ— æ³•ç†è§£çš„难题,而是以往尚未æ„识到的ç†å¿µã€‚å¸Œæœ›è¿™ä¸€ç ”ç©¶è¿›å±•èƒ½å¤Ÿä¸ºè®¤çŸ¥ç§‘å¦ä»¥åŠæ™ºèƒ½æŠ€æœ¯çš„å‘å±•èµ·åˆ°æŠ›ç –å¼•çŽ‰çš„ä½œç”¨ã€‚ æœ¬æ–‡ç”±äºŽç¯‡å¹…çš„åŽŸå› ï¼Œä¸å¾—ä¸çœå´äº†è®¸å¤šç»†èŠ‚。ä¸è¶³ä¹‹å¤„还望å„ä½è¯»è€…多多批评指æ£ã€‚
Since AC power cord is output of high voltage electric power, there is a risk of electric shock injury, therefore, All the AC power cord must comply with safety standard to produce. AC (Alternating Current) Power cord is to transmit high voltage. It is used to drive machinery or home appliances.
AC Power cord,power cable, batter cable, power cord
ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.wireharness-assembling.com