Speaking of power amplifiers, it is not unfamiliar to audio enthusiasts. However, for some friends who are new to the beginning or who have not yet started, it is often confusing to see the professional terms such as amplifiers, stone machines, preamps, rear amplifiers, and class D amplifiers.
In order to let more friends have more understanding of the power amplifier. The following home theater network is divided into three parts: the core device, function and working status of the power amplifier.

▌ According to the core amplifier component of the power amplifier
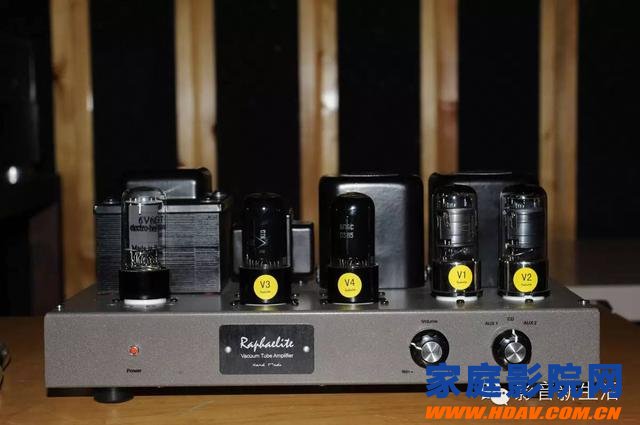
Tube power amplifier (amplifier)
Tube power amplifier, commonly known as the amplifier. The amplifier uses the tube as a core amplification component with a unique sound quality. The sound is warm and sound, the music is excellent, and the atmosphere is good. Since the electron tube is a voltage-controlled amplifier component, most of its distortion components are even-order distortion, which is exactly the octave harmonic in music performance. It sounds not only has no blunt distortion, but also has a soft and sweet flavor.

The tube power amplifier is especially suitable for playing idyllic soothing elegance of classical music and Chinese folk music. Especially in the performances such as (high mountain water), "fishing boat singing late", "Hu Yu 18 shot", "Pingsha Luoyan" and other zither guqin, the ethereal, transparent, full, elegant, there is indeed an extraordinary, unclean, I even found that I didn’t eat the fireworks and returned to the basics. Greatly welcomed by older generation enthusiasts.

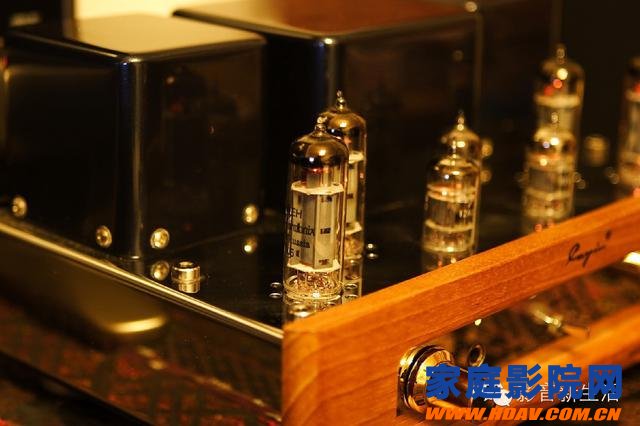
Transistor power amplifier (stone machine)
Transistor power amplifier, also known as stone machine. In the 1970s and 1980s, the amplifier was gradually eliminated due to the large size of the tube and the power consumption. Most of the tubes were replaced by small and power-saving transistors. The life of the transistor amplifier is very long, the sound is dynamic and fast, and it is obviously more suitable when expressing some large dynamic music. However, its sound is cold, especially the bass is not soft enough, and the high sound will appear sharp and so that it can not be loved by audiophiles.

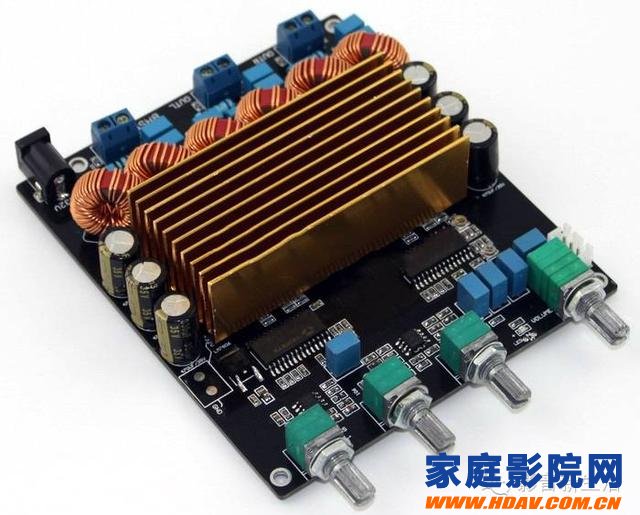
Integrated circuit power amplifier (IC amplifier)
The integrated circuit power amplifier is formed by integrating the main components of circuits such as OTL and OCL on a semiconductor chip, and a small number of external components can constitute a high-performance power amplifier. The integrated circuit has the advantages of small size, simple external circuit, good symmetry of internal components, complete protection functions, and low cost, so it is widely used in popular audio equipment. At present, professional audio power amplifiers almost all use an integrated power amplifier module as the output stage of the power amplifier.

▌ According to the function of the power amplifier
Preamplifier
A preamplifier is a circuit or electronic device placed between a source and an amplifier stage and designed to accept weak voltage signals from sources. Simply put, the function implemented by the pre-stage is to do the initial amplification of the signal and achieve volume adjustment. Most of the pre-stages are such active pre-stage circuits, rather than passive pre-stages that can only adjust the volume. Of course, in addition to adjusting the volume, the active front stage can also perform initial amplification and reduce the internal resistance between the sound source and the rear stage to buffer.

The role of the preamplifier is:
1. Improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the system (the front is placed close to the detector, the transmission line is short, the distributed capacitance Cs is reduced, and the signal-to-noise ratio is improved);
2, reduce the relative impact of external interference (signal pre-amplification);
3, reasonable layout, easy to adjust and use (pre-release is non-adjustable, main amplifier amplification adjustment multiple, forming constant);
4, to achieve impedance conversion and matching (preamplifier design for high input impedance, low output impedance).
Post power amplifier
The rear power amplifier is different from the preamplifier, which sends the signal from the front stage to the speaker and pushes the speaker to sound. The pure post-stage input signal is very simple, which is to take the output of the pre-stage and increase the power of the signal. The current stage is connected to a high-impedance post-stage that provides a suitable output voltage. The post-amplifier is connected to a low-impedance speaker that not only provides a suitable voltage, but also provides sufficient current. Therefore, a good after-stage system requires not only a high-power output, but also a large current design.

Combined power amplifier
The combined power amplifier is one of our most common power amplifiers, which combines preamplifier and power amplifier in one body. This amplifier has multiple sets of information source input selection, and has the level control function of the front stage, which combines the left and right channels. When the signal source is at a certain input level, the amplifier output can be full power load. Some consumer amplifiers we often see and use are combined designs that are relatively cost-effective compared to the use of front and rear amplifiers alone.

▌ According to the working state of the power amplifier
Class A Power Amplifier (Class A Power Amplifier)
Two (or two) transistors in the Class A amplifier output stage are always in a conducting state. When there is no signal, the two transistors each circulate an equal amount of current, so there is no unbalanced current or voltage at the output center point, so no current is input to the speaker. When the signal goes to the positive side, the output transistor above the line allows more current to flow in, and the lower output transistor reduces the current relatively. As the current begins to unbalance, it flows into the speaker and pushes the speaker to sound.

Class A power amplifiers work in such a way that they have the best linearity. Each output transistor amplifies the full-wave signal and there is no switching distortion. It is called the most ideal amplifying circuit design. However, this design has advantages and disadvantages. The biggest disadvantage of Class A power amplifiers is their low efficiency. Because there is still full current flowing in the absence of signal, all the energy is converted into high heat. As the signal level increases, some of the power can enter the load, but many still turn into heat.

Class A amplifiers are ideal for replaying music. They provide a very smooth sound quality, a rounded and warm tone, and a high-pitched transparent opening. These advantages are enough to compensate for its shortcomings. The cost of a pure class A power amplifier is also amazing, and its power consumption is equal to an air conditioner. Class A power amplifiers generate amazing heat. In order to effectively deal with heat dissipation, Class A power amplifiers must use large heat sinks. Therefore, the size and weight of the Class A machine are larger than those of the Class A and B, which increases the manufacturing cost and the price is relatively expensive.

Class B Power Amplifier (Class B Power Amplifier)
Class B amplifiers work in such a way that when there is no signal input, the output transistors are not conducting, so no power is consumed. When there is a signal, each pair of output tubes is amplified by half of the waveform, and each of the output tubes is turned on and off to complete a full-wave amplification, and crossover distortion occurs when the two output transistors are rotated, thus forming a nonlinearity.

Pure Class B amplifiers are less, because the distortion is very severe when the signal is very low, so the crossover distortion makes the sound rough. Class B amplifiers have an average efficiency of about 75%, which produces less heat than Class A machines, allowing the use of smaller heat sinks.

Class A and B power amplifiers (AB class amplifiers)
Class A and B power amplifiers are designed to combine the advantages of Class A and Class B power amplifiers, so that the advantages in performance are compromised. Class A and B power amplifiers usually have two bias voltages, and a small amount of current passes through the output transistors when there is no signal. It uses the Class A mode of operation to obtain the best linearity in the signal hour. When the signal is raised to a certain level, it automatically switches to the Class B mode for higher efficiency.

This design is a logical design with excellent sound quality and improved efficiency to reduce heat. Some Class A and B power amplifiers will adjust the bias current so high that they work in Category A over a wider power range, making the sound close to the pure Class A machine, but the heat generated is relatively increased.

Class C Power Amplifier (Class C Power Amplifier)
The bias of the gate of the Class C power amplifier causes the transistor to conduct for less than half of the time. When the driving signal is strong enough, the transistor will enter a saturated conduction state, output a pulse signal of the same frequency as the input signal, and the transistor turns on and off the power supply at the signal frequency, and the output signal will be seriously distorted with respect to the input signal. Because it contains many harmonic components of the input signal. Therefore, such amplifiers are very distorted and are only suitable for use in communication, and are not suitable for use in other audio systems.

D-type power amplifier (Class D amplifier)
Ding amplifiers, sometimes called digital amplifiers. It is an amplifier that drives the speaker by controlling the ON/OFF of the switching unit. The D-type amplifier was first proposed in 1958 and has gradually become popular in recent years. It has been published for many years, compared with the general linear Class A power amplifier circuit, the D-type power amplifier has high efficiency and small size.

The D-type power amplifier directly connects the load and the power supply, and the current distribution point output tube has no voltage, so there is no power consumption. When the output tube is turned off, all the power supply voltage will appear on the transistor, but there is no current and therefore no power consumption. In theory, its working efficiency is 100%. The D-type power amplifier has high efficiency and hardly produces heat. In theory, the distortion is small and the linearity is good. Dante class amplifiers work in a complicated way, and it is inevitable that there will be deviations in the increase of the line itself, so the really excellent D-class amplifier is not too much.

Appreciate the soothing and elegant classical music, we can choose the amplifier; in order to present the dynamic music, we can choose the stone machine; if the budget is limited and want to enjoy the high quality music, the IC amplifier is also a good choice; if the family karaoke is established, before Setting up a power amplifier is a must-have...
Conclusion: Each type of power amplifier is subject to factors such as materials, technology, design, etc. It is impossible to have all the advantages of various power amplifiers at the same time. When we understand the types of these amplifiers, we can better provide some reference for us to purchase and use the power amplifier. More fresh and fun home theater information, please pay attention to home theater network (WeChat: cnhifi) http://, the country's most influential home theater audio player interactive media website.
Circular Glass Panoramic Elevator
Elevator Panoramic,Circular Panoramic Elevator,Circular Glass Panoramic Elevator,Circular Panoramic Elevator With Glass
XI'AN TYPICAL ELEVATOR CO., LTD , https://www.chinaxiantypical.com