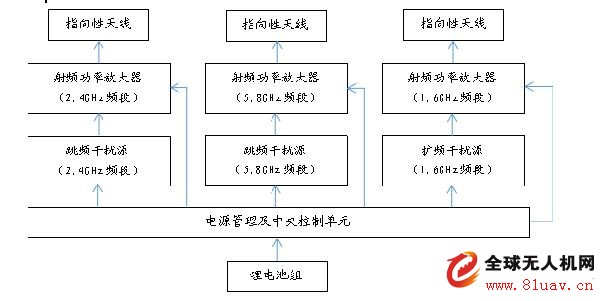
The device consists of a handheld main unit and a battery pack. The handheld host is designed as a three-band transmitter antenna, which can simultaneously generate UAV flight control interference signals and satellite positioning interference signals in the 2.4GHz/5.8GHz band, and through the uplink flight control channel and satellite positioning channel of the UAV . Blocking interference, so that it loses the flight control command and satellite positioning information, so that it can not fly normally. According to the design of the drone, it will produce the control effect of returning, landing and falling.
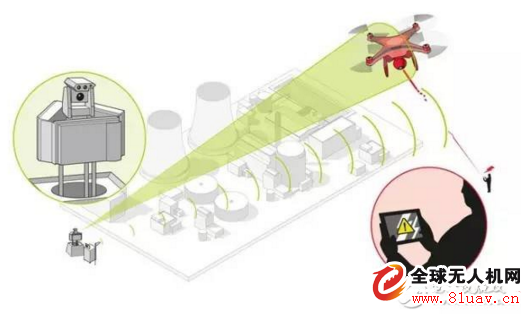
In the offensive and defensive situation, there is usually a distance between the operator of the drone and the sensitive area that needs to be fortified. The drone takes off from the vicinity of the operator and then gradually flies to the fortification area. When the drone reaches the vicinity of the fortification area and is capable of carrying out effective investigation or sabotage activities, the distance from the drone to the fortified area is usually much closer than it is to the operator.
In the above situation, all the uplink signals sent by the operator (transmitted from the ground to the drone) will be weak because of the distance. With the same power, the defender is closer to the drone and the signal will be stronger than the operator. The down signal received by the defender will also be stronger than the manipulator. However, the defense target for the downlink signal is that the operator does not receive it, and the distance from the drone to the operator is similar to the distance from the defender to the operator. Therefore, the blocking of the downlink signal does not occupy the terrain advantage.
From the above analysis, it can be seen that the interference uplink signal is more advantageous. It happens that the uplink signal is usually a remote control signal, which is directly related to the control of the drone. If the uplink signal is disturbed, the drone will lose its immediate control and can only operate according to the preset steps of the program (usually landing or hovering). The downlink signals are mainly telemetry and images. Although there may be sensitive information, it is less important than the control signal. In addition, the defender does not have an advantage in the situation, and usually adopts a laissez-faire attitude to the downlink signal.
GPS relies on medium orbit satellites. In general, the signal has reached tens of thousands of kilometers to reach the surface of the earth, which is already very weak. Therefore, it is relatively easy to interfere with the GPS signal when the drone is very close to the defender. If you want to deceive it, you need to use more complicated means to simulate GPS satellites, which is much more difficult.

At present, the control of the drone uses radio communication technology. By transmitting a high-power interference signal to the target drone and suppressing the control signal, the drone can be forced to land or return by itself.
The United States has taken advantage of this principle. The gun mounts an electronic jammer on the frame of the rifle. Once the trigger is pulled, the jammer will transmit a full-range interference signal to the drone, so that the drone is out of the operator's control and no control signal is received. Automatically landed on the ground.
Once the drone's signal is in a chaotic state, it usually has three choices: drop to the ground, return to the operator, or drop smoothly. This rifle has an effective range of 500 to 2000 meters.
At present, most consumer-grade drones prefer GPS navigation for flight control under normal conditions, while civilian GPS signals are unencrypted, leaving room for usable space.
The main principle of GPS spoofing is to send false geographic coordinates to the control system of the drone, thereby controlling the navigation system and inducing the drone to fly to the wrong place. The GPS signal can be generated by the generator or it can be recorded beforehand and then played back. Since the drone receives the GPS signal and always takes the strongest signal source, the artificial GPS signal on the ground can cover the real GPS signal from the space as long as the intensity is large enough to deceive the drone. GPS receiver module.
Currently, all countries have set up a no-fly zone in the core area, many UAV drone built factory business in firmware has been set, the UAV can not take off within the no-fly zone, even reaching the no-fly zone also Will land automatically. Therefore, as long as the ground artificial GPS signal simulates the geographic location as the coordinates of the no-fly zone, the drone can be forced to land on its own.

Nowadays, the control signals used by drones are mostly in the conventional civilian frequency bands of 1.2GHz, 2.4GHz, 5.8GHz, etc. With the rapid development of open source hardware such as Arduino and Raspberry Pi and the popularity of software radio (SDR) technology, ordinary fans It is also possible to use the hardware purchased from the network and the software source code obtained from the forum to simulate the remote control to send a control signal to the drone and cover the signal of the real remote controller to obtain control of the drone.
Many drones allow users to use mobile devices such as mobile phones and tablets to control and interact directly with Wi-Fi. In this way, some hacking technologies that are already mature on the Internet can be directly applied to drones.
For example, through the open port or password guessing in the drone control system, the control system is entered to realize the control of the drone. The legendary hacker Samy Kamkar who developed the "Sami worm" used this principle to write a drone hijacking software called "SkyJack" and install the software to a specially configured unmanned person. In the aircraft, SkyJack flies in the air and looks for other drones in the Wi-Fi range, then invades the drone and gains control.
Professionals engaged in anti-UAV applications in the industry said that the current domestic anti- UAV technology is still in the exploration stage. The radio hijacking technology is difficult to implement due to the encryption processing of radio signals by various UAV manufacturers. The threshold is not easy to commercialize, so the current technology is mainly based on interference blocking.
Suizhou simi intelligent technology development co., LTD , https://www.msmvape.com