Most of the mediums used in chemical production facilities are characterized by high toxicity, flammability, explosiveness, and strong corrosion. The operating conditions are complex and demanding, and the operating temperature and pressure are high. Once the valve fails, light leads to leakage of the medium, and severe causes the device to stop working. Discontinued production and even caused a vicious accident. Therefore, scientific and rational selection of valves can not only reduce the construction cost of the device, but also ensure the safe operation of production. Today, to talk about valve selection!
The main points of valve selection
1
Identify the use of the valve in the device or device
Determine the working conditions of the valve: the nature of the applicable media, working pressure, working temperature, and manipulation control methods.
2
Correct choice of valve type
The correct choice of valve type is based on the designer's full mastery of the entire production process and operating conditions. When selecting the valve type, the designer should first master the structural characteristics and performance of each type of valve.
3
Determine the end connection of the valve
The first two are most commonly used in threaded connections, flanged connections, and welded end connections. Threaded valves are mainly valves with a nominal diameter of 50mm or less. If the size of the ports is too large, the installation and sealing of the connections is very difficult.
Flanged valves are easier to install and remove, but they are bulkier and more expensive than threaded valves. Therefore, they are suitable for a wide range of pipe diameters and pressure connections.
The welded connection is suitable for more engraved conditions and is more reliable than flanged connections. However, it is difficult to dismantle and reinstall the welded connection valve, so its use is limited to the long-term reliable operation, or the use of conditions and high temperature occasions.
4
Valve material selection
The material of the housing, internal parts and sealing surfaces of the valve is selected, and in addition to considering the physical properties (temperature, pressure) and chemical properties (corrosiveness) of the working medium, the cleanliness of the medium (with or without solid particles) should be grasped. In addition to this, we must also refer to the relevant regulations of the country and the user departments.
Correct and reasonable choice of valve material can obtain the most economical service life and best performance of the valve. The sequence of the valve body material selection is: cast iron-carbon steel-stainless steel, and the order of the sealing ring material is: rubber-copper-alloy steel-F4.
5
other
In addition, the flow rate, pressure level, etc. flowing through the valve fluid should also be determined, and appropriate valves should be selected using existing data (such as valve catalogs, valve product samples, etc.).
Common valve selection instructions
1
Gate valve selection instructions
In general, gate valves should be preferred. The gate valve is not only suitable for steam, oil and other media, but also suitable for media containing granular solids and high viscosity, and is suitable for valves for venting and low vacuum systems. For media with solid particles, the gate valve body should have one or two purge holes. For low temperature media, low temperature special gate valves should be used.
2
Globe valve selection instructions
The cut-off valve is applicable to pipelines with strict requirements on fluid resistance, ie, little consideration for pressure loss, as well as high-temperature, high-pressure medium pipelines or devices, suitable for steam and other medium pipelines with DN < 200mm;
For small valves, stop valves can be used, such as needle valves, instrument valves, sampling valves, pressure gauge valves, etc.
The cut-off valve has flow regulation or pressure regulation, but it does not require high regulation accuracy, and if the pipe diameter is relatively small, shutoff valves or throttle valves should be selected.
For highly toxic media, bellows sealed shutoff valve should be used; but the cutoff valve should not be used for medium with high viscosity and medium with easy precipitation of particles, and it should not be used as valve for venting valve and low vacuum system.
3
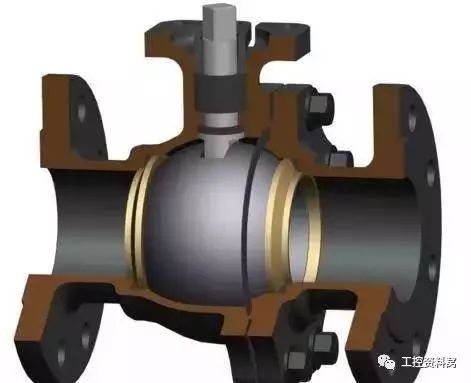
Ball valve selection instructions
Ball valve is suitable for low temperature, high pressure, high viscosity media. Most ball valves can be used in media with suspended solids and can also be used in powdered and granular media, depending on the material requirements of the seal;
All-pass ball valve is not suitable for flow regulation, but it is suitable for applications that require quick opening and closing, and is convenient for accidental emergency shutdown; usually has strict sealing performance, wear, shrinkage channels, rapid opening and closing action, high pressure cut-off (large pressure difference), Ball valves are recommended for pipelines with low noise, gasification, small operating torque, and low fluid resistance.
Ball valve is suitable for light structure, low pressure cut-off, corrosive medium; ball valve is the ideal valve for low-temperature, deep-cooled medium; low-temperature medium pipeline system and device should use low temperature ball valve with valve cover;
When the floating ball valve is selected, the valve seat material should receive the load of the ball and the working medium, and the large-diameter ball valve needs a large force during operation, and DN ≥
The 200mm ball valve should use the worm gear transmission; the fixed ball ball valve should be suitable for the occasions with large diameter and high pressure; in addition, the ball valve used for processing highly toxic materials and flammable medium pipelines should have fireproof and antistatic structure.
4
Throttle selection
Throttle valve is suitable for occasions with low medium temperature and high pressure. It is suitable for parts that need to regulate flow and pressure. It is not suitable for media with high viscosity and solid particles, and it is not suitable for the cut-off valve.
5
Plug valve selection instructions
Plug valves are suitable for applications that require quick opening and closing. They are generally not suitable for steam and high temperature media. They are used for low temperature, high viscosity media, as well as media with suspended particles.
6
Butterfly valve selection instructions
The butterfly valve is suitable for occasions with large diameter (such as DN>600mm) and short structure length, as well as occasions in which flow adjustment and opening and closing are required to be fast, generally used for temperature ≤
80 °C, pressure ≤ 1.0MPa of water, oil and compressed air and other media; due to the butterfly valve relative to the valve, ball valve pressure loss is relatively large, so the butterfly valve is suitable for pressure loss is not strict in the piping system.
7
Check valve selection instructions
Check valves are generally suitable for clean media and should not be used for media containing solid particles and high viscosity. When ≤40mm, it is better to use the lift check valve (only allowed to install on the horizontal pipeline); when DN=50~400mm, swing lift type lift check valve should be adopted (both horizontal and vertical pipelines can be installed, such as Installed on a vertical pipe, the flow of the medium is from bottom to top);
When DN ≥ 450mm, a buffer type check valve should be used; when DN = 100 ~ 400mm can also be used on the clip type check valve; swing check valve can be made of high working pressure, PN can reach 42MPa, Depending on the material of the housing and the seal, it can be applied to any working medium and any operating temperature range.
The medium is water, steam, gas, corrosive medium, oil products, medicines, etc. Medium operating temperature range of -196 ~ 800 °C.
8
Diaphragm valve selection instructions
Diaphragm valves are suitable for oils, water, acidic media, and suspension-containing media with working temperatures less than 200°C and pressures less than 1.0 MPa. They are not suitable for use in organic solvents and strong oxidizer media.
Abrasive granular media should be selected diaphragm diaphragm valve, use diaphragm diaphragm valve to refer to its flow characteristics table; viscous fluid, cement slurry and sedimentary medium should use straight-through diaphragm valve; in addition to specific requirements, diaphragm valve should not be used for vacuum tube Road and vacuum equipment.
Valve selection question and answer
1
Which of the three main factors should be considered by the selecting agency?
The output of the actuator is greater than the load of the valve and it is reasonably matched.
When checking the standard combination, consider whether the allowable pressure difference specified by the valve satisfies the process requirements. When the pressure difference is large, the unbalanced force of the spool is calculated.
It is necessary to consider whether the response speed of the actuator meets the process operation requirements, especially the electric actuator.
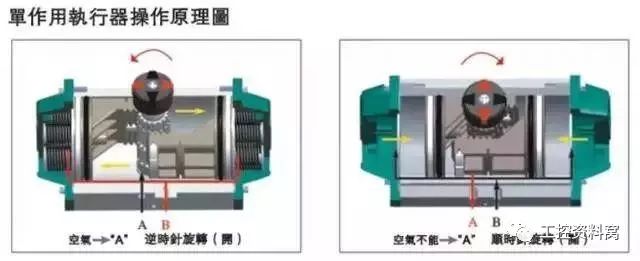
2
Compared with pneumatic actuators, what are the characteristics of electric actuators and what are the output formats?
The electric drive source is simple and convenient for power, thrust, torque, and stiffness. However, the structure is complicated and the reliability is poor. In the small and medium specifications more expensive than pneumatic. Commonly used in non-air source or without strict explosion-proof and flameproof. The electric actuator has three types of output modes: angular stroke, linear stroke, and multi-turn.
3
Why is the cut-off pressure difference of the angular stroke valve larger?
The cut-off pressure difference of the angular stroke valve is larger because the resultant force generated by the medium on the valve plug or the valve plate generates a very small torque on the rotating shaft, so that it can withstand a large pressure difference. Butterfly valves and ball valves are the most common types of quarter-turn valves.

4
Which valves need to be selected for flow? how to choose?
Single-seal type control valves such as single-seat valves, high-pressure valves, and single-sealing sleeve valves without balancing orifices require flow direction selection. Open and closed flow have advantages and disadvantages. The open-type valve works relatively stable, but has poor self-cleaning performance and tightness, and has a short life. The flow-closed valve has a long life, self-cleaning performance and good sealing performance, but when the diameter of the valve stem is smaller than the diameter of the valve core, the stability is poor. .
Single seat valve, small flow valve, single seal sleeve valve is usually selected to open, when the flushing or self-cleaning requirements can be selected flow closure. Two-type quick opening characteristics control valve selection flow closed type.
5
In addition to single, double seat valve and sleeve valve, which have the function of the valve?
Diaphragm valves, butterfly valves, O-ball valves (mainly based on cutting), V-ball valves (larger adjustment ratio, shearing action), and eccentric rotary valves are all valves with adjusting functions.
6
Why is the selection more important than the calculation?
Compared with the calculation and selection, the selection is much more important and more complex. Because the calculation is just a simple formula calculation, it is not the accuracy of the formula itself, but the accuracy of the given process parameters.
There are many items involved in the selection, and careless selection will result in inappropriate selection. This not only results in a waste of manpower, material resources, and financial resources, but also results in unsatisfactory results, and brings with it certain problems in use, such as reliability, longevity, and operation. Quality and so on.
7
Why can't dual seal valve be used as shut-off valve?
The advantage of the double seat valve spool is that the force balance structure allows a large pressure difference, and its outstanding disadvantage is that the two sealing surfaces cannot be in good contact at the same time, resulting in large leakage.
If it is artificially and forcibly used to cut off the occasion, obviously the effect is not good, even if it has made many improvements (such as double sealed sleeve valve), it is also not desirable.
8
Why does a double seat valve easily oscillate when it is operated at a small opening?
For a single core, when the medium is a flow-open type, the valve has good stability; when the medium is a flow-closed type, the stability of the valve is poor. The double seat valve has two spools, the lower spool is closed and the upper spool is open.
In this way, when the valve is operated at a small opening degree, the flow-closed valve element can easily cause the vibration of the valve, which is why the double-seat valve cannot be used for a small opening degree work.
9
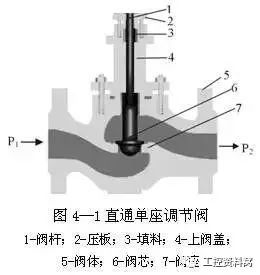
What are the characteristics of straight-through single seat regulators? Where is the application?
The discharge flow is small because only one spool is easy to seal. Standard discharge flow is 0.01% KV, and further design can be used as shut-off valve.
The allowable pressure difference is small because of the large thrust of unbalanced forces. The valve ΔP of the DN100 is only 120KPa.
Small circulation capacity. The KV of the DN100 is only 120. It is often used in applications where leakage is small and pressure difference is not large.
10
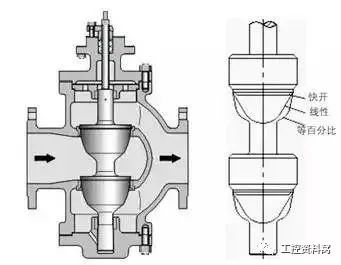
What are the characteristics of straight-through two-seat control valve? Where is the application?
The allowable pressure difference is large because many imbalance forces can be offset. The valve ΔP of the DN100 is 280 KPa.
Large circulation capacity. The KV of the DN100 is 160.
The amount of leakage is large due to the fact that two spools cannot be sealed at the same time. The standard discharge flow is 0.1% KV, which is a multiple of the single seat valve 10 . Straight through two-seat regulating valve is mainly used in occasions where high pressure difference is not required and leakage is not strict.
11
Why does the straight stroke control valve have poor anti-blocking performance and the angular stroke valve has good anti-blocking performance?
Straight stroke valve spool is vertical throttling, and the medium is horizontal flow in and out, the flow path in the valve cavity will inevitably turn and turn, so that the flow path of the valve becomes quite complex (shape is like inverted "S" type). In this way, there are many dead zones, which provide space for the sedimentation of the media and, over time, cause blockages.
The throttle valve throttle direction is the horizontal direction, the media flow into the horizontal outflow, easy to take away the dirty media, while the flow path is simple, the medium precipitation space is also very little, so the angle valve anti-blocking performance is good.
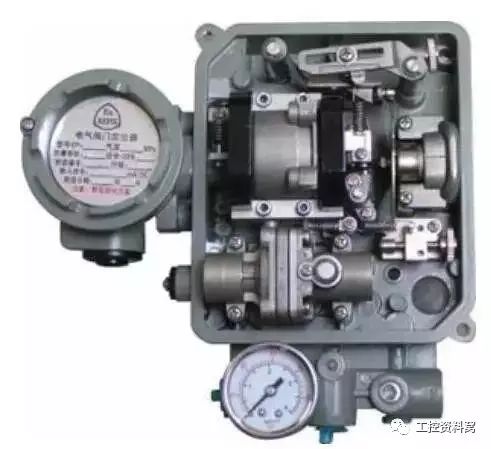
12
Under what circumstances need to use the valve positioner?
Friction is great and needs precise positioning. For example, high temperature, low temperature control valve or adjustment valve using flexible graphite packing;
The slow process needs to improve the response of the valve. For example, temperature, level, analysis and other parameters of the adjustment system.
Need to increase the output force and cutting force of the actuator. For example, single seat valves with DN ≥ 25, double seat valves with DN > 100. Valve pressure drop △ P> 1MPa or inlet pressure P1> 10MPa occasions.
In the operation of the split-range control system and control valve, it is sometimes necessary to change the form of air-opening and air-closing.
Need to change the valve flow characteristics of the occasion.

13
What are the seven steps to determine the diameter of the regulating valve?
Determine the calculated flow - Qmax, Qmin
To determine the pressure difference - select the resistance ratio S according to the system characteristics, and then determine the pressure difference when calculating (the valve is fully open);
Calculate the flow coefficient - select the appropriate calculation formula chart or software to find the max and min of KV;
KV value selection - according to the KV max value in the selected product series is the closest to the first KV, get the primary caliber;
Checking the opening degree - 90% valve opening when Qmax is required; 10% valve opening when Qmin;
Checking the actual adjustable ratio - General requirements should be 10; R actual> R requirements
Determination of caliber - if unqualified re-election KV value, and then verify.
14
Why sleeve valve instead of single, double seat valve but did not do it?
The sleeve valves that came out in the 1960s were widely used at home and abroad in the 1970s. The proportion of sleeve valves in petrochemical plants introduced in the 1980s was relatively large. At that time, many people believed that sleeve valves could replace single and double valves. Seat valve, becoming the second generation product.
Until now, this is not the case. Single-seat valves, double-seat valves, and sleeve valves have all been used equally. This is because the sleeve valve only improves the throttling type, stability and maintenance better than single seat valve, but its weight, anti-blocking and leakage indicators are consistent with single and double seat valves. How can it replace single and double seat valves? What? Therefore, they can only be used together.

15
Why cut off the valve should try to use a hard seal?
The cut-off valve requires a lower leakage, the better, and the leakage of the soft-seal valve is the lowest. The cut-off effect is certainly good, but it is not wear-resistant and has poor reliability. From the double standards of small leaks, sealing and reliability, soft seal cutting is not as good as hard seal cutting.
Such as full-featured ultra-light control valve, sealed and piled with wear-resistant alloy protection, high reliability, leakage rate of 10 to 7, has been able to meet the requirements of the shut-off valve.
16
Why is the straight stroke valve stem smaller?
It involves a simple mechanical principle: large sliding friction and low rolling friction. The valve stem of the linear valve moves up and down, and the packing is pressed slightly. It will pack the valve stem tightly and generate a large return difference.
For this reason, the valve stem is designed to be very small, and the filler is often a PTFE filler with a small friction coefficient in order to reduce the return difference, but the problem is that the valve stem is thin, it is easy to bend, and the filler life is short.
To solve this problem, the best way is to use the trip valve stem, which is a quarter-rotor type control valve, its stem is 2 to 3 times thicker than the straight stroke stem, and the use of long-life graphite filler, stem rigidity Well, long filler life, the friction torque is small, the difference is small.
Want more people to understand your experience and experience at work? If you are engaged in equipment technical work, have knowledge on the use of valve maintenance and other aspects, you can communicate with us, maybe your experience Will help more people.
Wuxi Lerin New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.lerin-tech.com