Introduction
What is the robustness of ON Semiconductor, the operating temperature range, and how is high electrical noise handled? What about ESD and fault protection? These questions are not necessarily the first thing a design engineer thinks when choosing an IC. Despite this, robustness is a key performance parameter for long-running and reliable, reputable high-end products. This is especially true when the harsh working environment is a common industrial environment design system. Industrial equipment that can be exposed to a wide range of temperature, high electrical noise power lines or data lines, such as ESD or short circuit fault events.
Today, the temperature standard of integrated circuits in industrial environments is -40 ° C to +85 ° C, the temperature range of "expansion" + 15 ° C is higher than the standard -40 ° C to +70 ° C years ago . The industry trend is to work at higher and higher temperatures, and eventually the new expectations will be in the automotive industry at -40 ° C to +125 ° C. The higher current and power density make it obvious that IC companies must design circuits to withstand a wider temperature range... the decision-making process that is left out.
Processing voltage transients
Voltage transient power lines often appear because of incorrect wiring or accidental shorts. These transients can damage downstream circuits if the inputs are not guaranteed. Series fuses with transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diodes constitute a simple and discreet circuit that has traditionally been used to protect against most transient voltages (Figure 1).
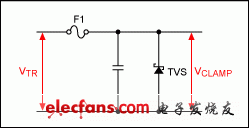
figure 1. The transient voltage protection circuit uses a discreet component.
Transient protection uses a discreet component, however, it has its own limitations. TVS diode protection thresholds are often not well controlled and can vary dramatically with temperature. In addition, after an overvoltage condition occurs, the fuse needs to be replaced. Finally, large transients require a large amount of TVS diodes to consume board space and consume extra heat.
More control methods to manage overvoltage and transient events are the integration of protection thresholds and reactive circuits into an integrated circuit. Each time to ensure a reliable response, the internal comparator and diode are supervised and protected by the IC design. Some integrated circuits integrate high voltage fault protection for data lines. In order to protect itself from damage, the fault protection device will lock out when it exceeds the voltage level of the normal data line. An example of this is the MAX4708 multiplexer family. The MAX4708/MAX4709 include two fault detections: a high side above the active rail NO_ voltage detector (V + ), and a low side detector NO_ below the negative rail voltage (V) (Figure 2). When the NO_ voltage exceeds the supply rail, at this point, the FETs of N1 and P1 are both turned off and a fault condition occurs. This happens when this method quickly disconnects the input and output switches.
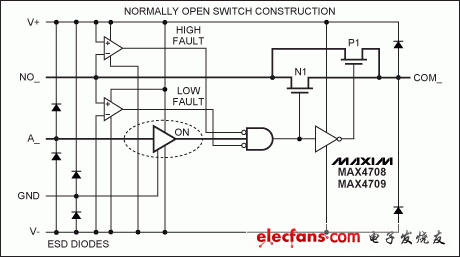
figure 2. Functional block diagram of the MAX4708/MAX4709.
With RS-485 transceivers, voltage transients in data systems can also be managed. The receiver input and output drivers, an RS-485 transceiver, may be exposed to significantly higher voltages within the specified range than the -7V to +12 V common mode EIA/TIA-485 standard industrial system. The new transceivers have been designed to withstand these voltage events and can now withstand up to ±80V (ground) without damage. The state-of-the-art technology of this country ensures reliable protection and longevity.
Prevent ESD and malfunction
Integrated ESD circuitry protects against damage to IC ESD events and helps make the overall system more robust.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD), when another overvoltage event occurs, the two materials have different potential contacts, transporting stored static charge, and generating sparks. The interaction between people and the surrounding environment often produces static sparks. These unintentional sparks can alter the performance of a semiconductor device, reducing or completely destroying it. ESD is a serious industrial problem that is estimated to cause billions of dollars in damages each year. ESD events occur in a single component failure in a business area, sometimes even a catastrophic system failure.
ESD diodes and other types of protection data lines for external discrete component circuits can be used. Many IC devices integrate some degree of ESD protection IC itself without further external protection. Figure 3 shows a very simplified functional block diagram, a common comprehensive protection plan. The spike voltage signal input/output (I/O) is clamped to V CC or GND and protects the internal circuitry. Many interface products and analog switches, integrated ESD protection design in accordance with IEC 1000-4-2 standards. It is worth noting that Maxim recently obtained its PROFIBUS RS-485 transceiver with an ESD Human Body Model (HBM) level of ±35 kV MAX14770E.
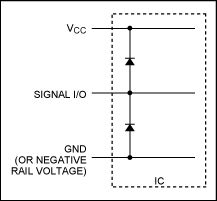
image 3. Simplify the integrated ESD protection circuit.
in conclusion
While robust operating temperature ranges, ESD and short circuit faults and line protection cover design issues from different groups, it is not usually the first thing that is the design engineer address. This can be a serious mistake. Applications in the industrial market require powerful components to withstand harsh environments and territories. Robustness should be considered early in the design phase of these applications.
Direct Driven Servo Motors,Direct Drive Motor,Ac Motor Integrated Servo,Ac Three Phase Servo Motor
Zhejiang Synmot Electrical Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.synmot-electrical.com