Have you evaluated the noise performance of an ADC and found that the measured performance is different from the rated performance given in the device datasheet? Achieving high resolution in high-accuracy data acquisition systems requires some knowledge and understanding of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) noise. It is necessary to understand how the data sheet specifies noise performance and how external noise sources affect overall system performance. One example of a noise source is my colleague Ryan Andrews in his blog post, “Caution! Your ADC's performance may be just about the same as its power performance.†In this blog post, I'll take a look at how reference noise affects DC noise performance in an incremental-accumulating ADC.
As shown in Figure 1, you can specify and measure the DC noise performance of an ADC with positive and negative inputs that are shorted to the midsupply voltage. By measuring the noise under this condition, the noise in the ADC output code is hardly affected by variations in the reference voltage, reference noise, or input signal noise. Although this test condition is an over-optimal situation relative to the actual application, it does give a good ADC noise performance that is not affected by some external noise sources.
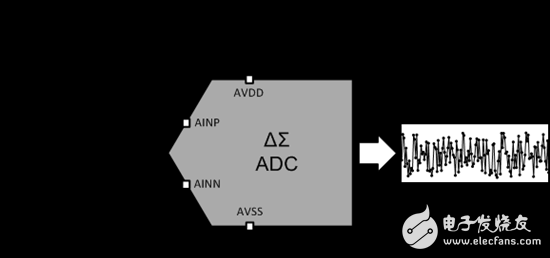
Figure 1: ADC noise performance test (and debug) configuration
Tip: When debugging, start evaluating the system's noise performance with a short-circuit input test to evaluate the noise performance of an isolated ADC before starting other system noise performance tests.
How Reference Noise Affects ADC DC Noise Performance
This effect is related to the basic task of the ADC; the basic task of the ADC is to provide an output code that represents the ratio of the input signal voltage to the reference voltage. Both the input and the reference voltage add a noise term to this ratio, as shown in Equation 1:
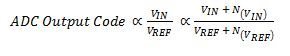
(1)
Input signal noise,
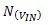
The effect on the ADC conversion result is very straightforward. The ADC will capture any noise that has not been filtered out using an external resistor-capacitor (RC) filter, or a signal filter of an incremental-accumulated ADC. due to
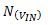
There is a direct effect on the ratio in Equation 1, which you can observe in the output code.
Tip: When evaluating ADC noise performance, make sure the input signal is a low noise source because the noise of the input signal directly affects the output of the ADC.
However, the reference noise,
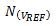
The effect on ADC conversion results is not straightforward because
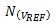
Appears in the denominator. When the numerator is zero (as in the case where the ADC input is shorted), this ratio is always zero, and
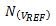
Items will not affect the ratio. When the numerator and denominator are roughly equal,
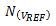
Will have a great influence on the ratio. When the ratio is between 0 and 1,
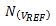
The impact is measured by the ratio value. Figure 2 shows the resulting behavior of the feature.
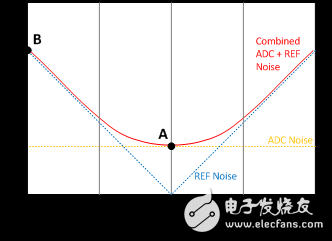
Figure 2: Relationship between ADC and Reference Noise vs. Input Voltage
When the reference noise is added to the noise of the ADC by using the rms increase method, this combined noise is a function of the input voltage and it increases when the positive or negative input voltage becomes large. On the curve in Figure 2, there are several points to note:
Point A, which is the ADC noise measured with the short input given in the ADC datasheet.
Point B, which is the total bandwidth limiting reference noise, is usually limited by the ADC digital filter bandwidth.
If you know the noise spectral density and noise bandwidth for the noise source, you can calculate the reference noise (point B); otherwise, apply a full-scale voltage input to the ADC and measure the noise performance, which is usually obtained A good baseline noise measurement.
How to select a reference
A low noise reference is very important for low noise/high resolution performance over the entire ADC input range. The reference noise requirement will depend on the system's target resolution, input signal range, and data rate (which typically limits the input and reference noise bandwidth). When the noise bandwidth is limited by slower data rates, or the input signal span is limited to a small range within the full-scale range of the ADC, the system can tolerate additional reference noise.
Many delta-sigma ADCs include an integrated reference that provides sufficient performance for most applications. For more demanding applications, using an external reference may improve the noise performance when the input is near the positive and negative full-scale ranges. External precision reference can achieve lower noise performance because of their higher power consumption. Figure 3 compares the noise performance of the 24-bit ADS1259 delta- accumulating ADC with the internal reference, an external REF5025 voltage source, and a scaled reference source.
Figure 3: ADS1259 Noise Performance with Internal, External, and Scaled Reference Sources
Although the external reference may be able to achieve better noise performance than the integrated reference, the scaling reference configuration performs better. A scaled configuration uses the same voltage source for reference voltage and input signal excitation. By sharing a common voltage and noise source, the sum in Equation 1 tends to cancel each other in the ratio.
When you next evaluate the noise performance of the ADC, make sure to take into account the effects of the reference noise. In addition, as long as the sensor requires an excitation source, the implementation of scaling measurement should be your first choice.
The 7-inch tablet can be used as the golden size of a tablet computer. It is small and portable. It can be used at home and outdoors. You can browse the web, watch videos and play games. It is a household artifact. Although the size of the 7-inch tablet is inclined to the tablet, the function is more inclined to the mobile phone, so it can also be used as a substitute for the mobile phone. Compared with other sized tablets, the 7-inch tablet has obvious advantages in appearance and weight. Both the body size and the body weight have reached a very reasonable amount.
1.In appearance, the 7 inch tablet computer looks like a large-screen mobile phone, or more like a separate LCD screen.
2.In terms of hardware configuration, the 7 inch tablet computer has all the hardware devices of a traditional computer, and has its own unique operating system, compatible with a variety of applications, and has a complete set of computer functions.
3.The 7 inch tablet computer is a miniaturized computer. Compared with traditional desktop computers, tablet computers are mobile and flexible. Compared with Laptops, tablets are smaller and more portable
4.The 7 inch tablet is a digital notebook with digital ink function. In daily use, you can use the tablet computer like an ordinary notebook, take notes anytime and anywhere, and leave your own notes in electronic texts and documents.
7 Inches Tablet Pc,Quad Core Tablet 7 Inch,7 Inch Gaming Tablet,Supersonic Tablet 7 Inch
Jingjiang Gisen Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.gisengroup.com