Some circuits use flip-flops that have both active and inactive states. Once the circuit enters an inactive state, it goes to the point. After the power failure or the interference signal causes the circuit to enter an inactive state, the circuit continues to cycle in an inactive state, and it is critical that the circuit automatically returns to the active state. Only the circuit that can be returned to the active state after restarting is called a circuit that cannot be self-started, and the circuit that automatically returns to the active state without restarting is called a self-starting circuit. For example, the ring counter has an invalid state, and the connection method is different, and there is a function that cannot be self-started and self-started.
Simply put, the state of the circuit has two types: active state and invalid state. When the circuit enters the invalid state due to interference or other reasons, it can automatically enter the active state, which is called self-starting capability, otherwise it is called no self-starting capability.
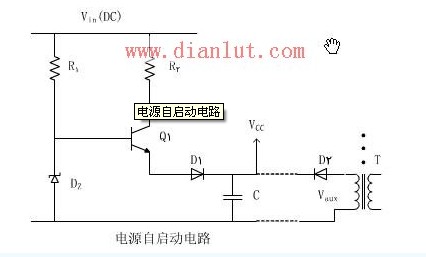
The circuit is a high voltage, current limited linear power supply. During the stable operation of the circuit, the diode and base on the emitter are reversed, thus completing the startup current cut-off process. The VCEO (SUS) of a small signal transistor is required to be higher than the input voltage, and almost all of the loss is consumed by the resistance of the collector. During regulation, only a small bias current flows through the base of the transistor and the Zener diode.
Other household electric appliance
gree , https://www.greegroups.com