The power management design of the Bluetooth headset requires fewer peripheral components and high integration, while meeting the Bluetooth chip's requirements for load response and noise suppression. Wireless stereo headphones have become a hot product. As more and more phones support Bluetooth, Bluetooth headsets have become a must-have option for mobile phones. At the same time, with the introduction of stereo Bluetooth headsets that support MP3 playback, Bluetooth headsets have been able to connect to Bluetooth mobile phones and music players at the same time, which will definitely bring new highlights to Bluetooth applications.
The core of the Bluetooth headset is RF and baseband processing. In order to adapt to the integration of functions and miniaturization of design, CSR, Broadcom and other companies have integrated RF and baseband processing functions, such as CSR BlueCore4 highly integrated Bluetooth chip, the smallest package For 6&TImes; 6mm. The power management design of the entire headset requires fewer peripheral components and high integration, while meeting the Bluetooth chip's requirements for load response and noise suppression.
Figure 1: Application circuit of the TC1303 on a Bluetooth headset.
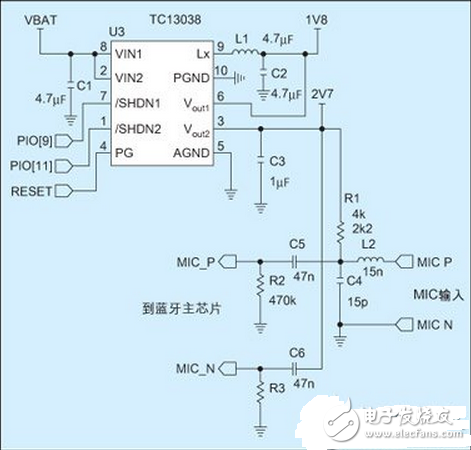
Bluetooth headsets are mostly powered by lithium batteries and have a voltage range of 2.7V to 4.2V. The battery capacity is 90mAH to 170mAH. In order to meet the needs of longer talk and music playback, the battery capacity has gradually increased. In addition, Bluetooth chips based on ARM or DSP cores require two sets of power supplies (such as 1.8V and 2.7V) to power the core and I/O respectively. At the same time, the microphone also requires a "clean" bias voltage.
Based on the above system power requirements, Microchip has introduced a highly integrated, small-scale power management solution, including the TC1303 and MCP73855. Among them, TC1303 is a highly integrated power conversion chip, MCP73855 is a highly integrated linear lithium battery charging chip. The TC1303 integrates a 500mA synchronous buck converter and a 300mA low dropout LDO in a 3&TImes; 3mm 10-pin DFN package with a voltage-good indicator pin (Power-Good). Its standard fixed voltage output combination, such as 1.8V/2.7V, meets the power requirements of BlueCore2. Figure 1 shows the application circuit of the TC1303 on a Bluetooth headset.
The 500mA synchronous DC/DC converter in the figure integrates P-channel and N-channel MOSFETs with a switching frequency of 2MHz and a conversion efficiency of over 92%. High switching frequency and PWM/PFM automatic switching technology allow engineers to select surface-mount inductors and ceramic capacitors as low as 2.2μH to meet the ripple requirements of filtering and Bluetooth chips. The integrated LDO in the TC1303 provides an output current of 300mA with a voltage difference of only 137mV. In order to further reduce the impact of DC/DC switching noise on the circuit design, the LDO's power ground pin and DC/DC power ground pin are separated during chip design, ensuring that the LDO output can provide I/O parts and microphones. Clean" voltage.
Figure 2: Application circuit of MCP73855 in Bluetooth headset design.
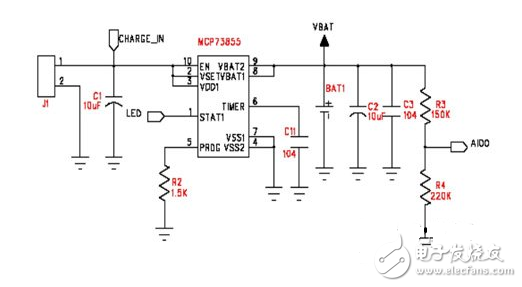
The voltage normal indicator pin provided by the TC1303 can be connected to the I/O of the Bluetooth chip to monitor the status of the supply voltage. The voltage normal indication pin can detect the DC/DC output voltage (TC1303A) or the LDO output voltage (TC1303B), and can even detect the two outputs separately to achieve sequential power-on, which satisfies the requirements of different Bluetooth chips for power supply. The MCP73855 provides lithium battery charge management. The on-chip integrated MOSFET, current sense resistor and reverse blocking diode provide up to 400mA of charge current and can be set by an external resistor or directly from the I/O output. . The MCP73855 automatically completes the precharge, constant current, and constant voltage charge control of the lithium battery and outputs the charge status to the LED or Bluetooth chip. With appropriate peripheral circuits, the charge status indicator pin can drive a two-color LED to achieve separate display of the charging process and charging end. Figure 2 shows the application circuit of the MCP73855 in the Bluetooth headset design.
The TC1303 and MCP73855's small package (3&TImes; 3mm) and simple peripheral circuits form a low-cost, high-performance, highly integrated Bluetooth headset power management solution, which is also suitable for the latest Bluetooth stereo headset design for MP3 playback. . Engineers and Bluetooth chips can be used to design a more comfortable, stylish, easy-to-use, lightweight Bluetooth stereo headset that allows users to enjoy music while on the move, and never miss a call.
In fact, what people usually call a pinhole camera does not use a pinhole lens. Pinhole lens refers to a lens that uses the principle of small hole imaging to obtain images. It is inexpensive and simple in principle, but its fatal weakness is that too little light passes through the small hole, resulting in too long exposure time. Taking photos with a pinhole lens in sunlight can take anywhere from a few minutes to a dozen minutes, especially when shooting at night with exposure times of up to several hours. Obviously, for a camera that shoots dozens to dozens of frames per second, it cannot meet the requirements. Pinhole lenses cannot be applied to cameras, so there is no "pinhole" camera in the strict sense. As is customary, a miniature camera using a fisheye lens, a flat lens or a conical lens is called a pinhole camera.
According to the lens, the lens of the pinhole camera can be divided into three types: fisheye lens, flat lens and conical lens; according to the photosensitive element used, it can be divided into charge coupled element and complementary metal oxide semiconductor; According to the data transmission method, it can be divided into two categories: wireless cameras and wired cameras.
Jingjiang Gisen Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.gisengroup.com