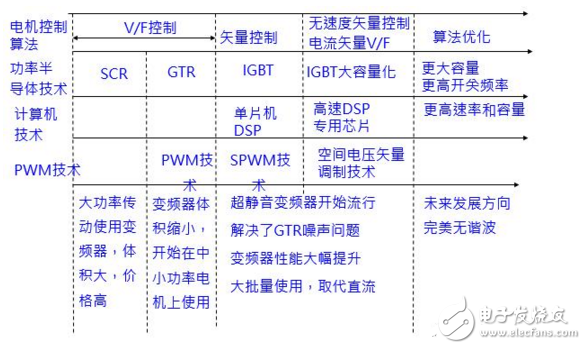
The frequency converter is an AC speed regulating device developed from the middle of the 20th century. It is to solve the problem that the traditional AC motor speed control is difficult, the speed control equipment has complex structure and the efficiency and reliability are not satisfactory.
1, the frequency converter
Inverter: VVVF (Variable Voltage Variable Frequency) is an AC speed regulating device developed from the middle of the 20th century. It is to solve the difficulty of traditional AC motor speed regulation. The structure of the speed control equipment is complex and the efficiency and reliability are not satisfactory. The shortcomings appear;
Since the frequency converter makes the speed regulation range and speed regulation performance of the AC motor greatly improved, the AC motor gradually replaces the DC motor in various application fields, even including the field of AC servo control;
The control object of the inverter: three-phase AC asynchronous motor and three-phase AC synchronous motor, the standard matching motor pole number is 2/4/8 pole;

Inverter electric drive system
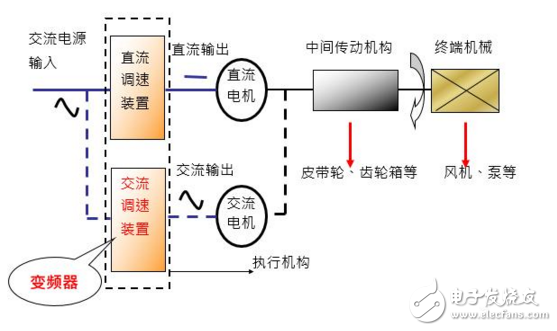
2, the inverter features
1) Very good value for money;
2) Easy to operate;
3) The mechanical properties are hard and the static rate is small;
4) The speed stability is good;
5) The advantages of wide speed range and other advantages.
3, frequency converter application field
Electric drive system load characteristics
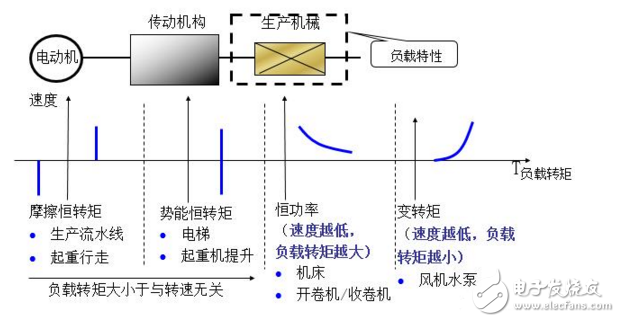
4, the working principle and control method of the inverter
The formula for the speed of the AC motor is:
N=60f(1-s)/p
Where: f—frequency;
P—pole logarithm;
S—slip rate (0 to 3% or 0 to 6%);
4.1. Frequency control principle
Inverter: Change the power frequency of the three-phase asynchronous motor, you can change the synchronous speed to achieve the purpose of speed regulation.
The rated frequency is called the fundamental frequency. When the frequency conversion is adjusted, it can be adjusted upward from the fundamental frequency (constant power speed regulation), or it can be adjusted downward from the fundamental frequency (constant rotation speed regulation). Therefore, the variable frequency speed control mode is much simpler than changing the two parameters of the pole log p and the slip rate s.
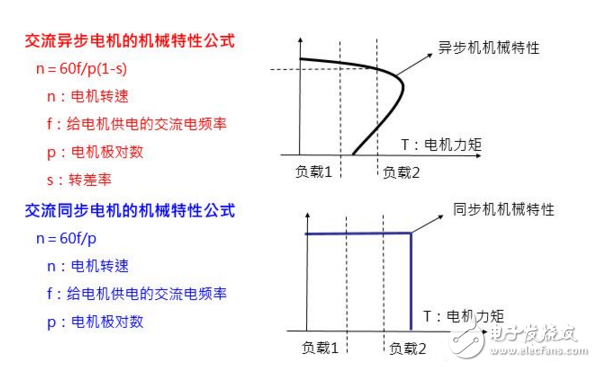
4.2. Inverter control algorithm
The core of the AC speed control is: only to keep the motor flux constant to ensure the output of the motor, in order to obtain the desired speed control effect;
V/F control - simple and practical, general performance, most widely used, as long as the output voltage and output frequency are constant, the flux can be kept at a constant low frequency, the stator voltage drop will cause the magnetic flux to drop, and the output voltage needs to be appropriate. improve;
Vector control - excellent performance, comparable to DC speed control, late maturity, mimicking the control method of DC motor, using vector coordinate transformation to achieve decoupling control of stator excitation current component and torque current component of asynchronous motor, keeping The motor flux is constant, which in turn achieves good torque control performance for high performance control. Excellent performance and the same complexity of control;
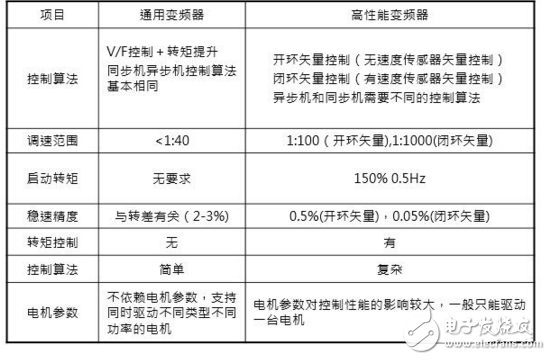
4.3. Frequency converter technology development
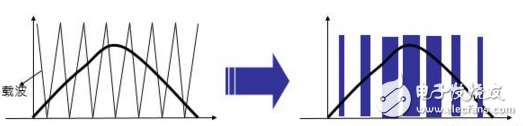
PWM (Pulse Width ModulaTIon) modulation
The PWM modulation is to modulate the DC voltage into a voltage-variable, variable-frequency voltage pulse train by turning on and off the semiconductor switching device.
· SPWM modulation is: PWM waveform obtained by the intersection of triangular wave and sine wave directly controls each switch to obtain the output pulse voltage of pulse width and sinusoidal variation with variable duty ratio between pulses, which can achieve ideal control effect: Output current is approximately sinusoidal
· The carrier frequency must be high to ensure that the waveform obtained after modulation has the same effect as before the modulation
·GTR inverter has a high switching noise because the switching frequency is too low, and the IGBT effectively solves this problem.
4.4. Basic structure of the inverter
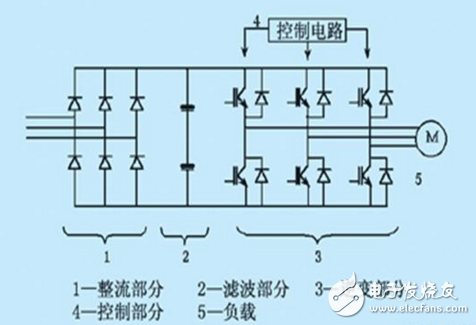
The basic circuit of the general-purpose inverter is shown in the figure above. It consists of four main parts, namely:
1—rectification part: a power electronic device that converts an alternating current voltage into a direct current voltage; converts alternating current into a direct current, the input voltage is a sine wave, and the input current is non-sinusoidal with harmonics;
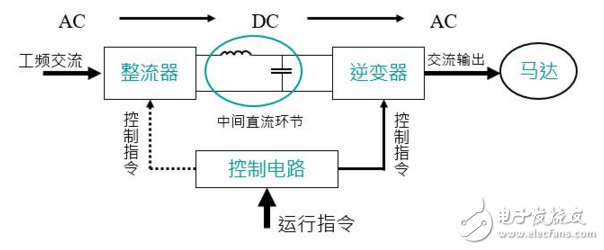
2—Filtering part: filtering the pulsating DC power into a relatively smooth DC power;
3—Inverter part: converts DC power into three-phase AC power. This inverter circuit is generally a PWM wave modulated by the power switch component according to the driving of the control circuit and the output pulse width, or a sinusoidal pulse width modulation SPWM wave. When the voltage of this waveform is applied to the load, the current is continuous due to the action of the load inductance, and becomes a current waveform close to the sine wave;
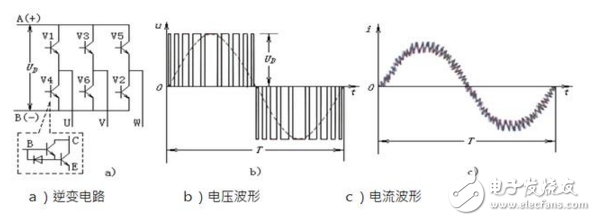
4—Control circuit: used to generate the driving signals required for the output inverter bridge. These signals are determined by external commands, with frequency rise and fall, external on/off control, and various protection and feedback inside the inverter. Integrated control of signals, etc.
Bakelite Material,Bakelite Plastic,Bakelite Made From,Bakelite Synthetics
WENZHOU TENGCAI ELECTRIC CO.,LTD , https://www.tengcaielectric.com