The significance of wireless charging is to charge the battery. If you don't understand the battery, don't talk about charging, let alone wireless charging. If you want to know about wireless charging, first understand the battery. The battery mentioned here mainly refers to the lithium battery. Only the basics of the battery are introduced here, suitable for all practitioners in the wireless charging industry.
Too many people have misunderstandings about batteries, etc.:
Misunderstanding 1: Whether the battery needs to be activated, whether the new battery needs to be charged and discharged repeatedly 3 times, each time charging for 12 hours.
Myth 2: The battery is charged as little as possible, and the service life is long.
Myth #3: When the battery is charged for too long, it will explode. If it is full, it will be unplugged.
Myth 4: The faster the battery, the better the battery.
Myth 5: The higher the charging current of the charger, the faster the charging.
Myth 6: Wireless charging is not as fast as wired charging.
Let's not discuss the reasons for these misunderstandings. Below we analyze the characteristics of lithium batteries and naturally understand the specific reasons.
The full text is divided into three major sections: battery basics, battery protection, and battery charging.
(1) Lithium battery foundation
Composition of lithium battery
The mobile phone batteries we usually see are all lithium batteries. The industry is more battery PACK. The lithium battery PACK is mainly composed of two large blocks: the battery core and the protection board. The battery core is mainly composed of five blocks: a positive electrode material, a negative electrode material, an electrolyte solution, a separator and an outer casing. The protection board is mainly composed of a protection chip, a MOS tube, a resistor capacitor and a PCB board.

Lithium battery classification
Lithium batteries are classified into cylindrical batteries and square batteries according to their shapes. Cylindrical type is 18650 battery for mobile power and power tools, square battery such as mobile phone battery.
According to the electrolyte, it is divided into a lithium ion battery and a polymer battery. Lithium-ion battery electrolyte is liquid, and the outer casing is generally hard, usually aluminum or steel. For example, Samsung's traditional machines are lithium-ion batteries. The polymer battery electrolyte is solid, such as the battery of an Apple mobile phone.

Common terms for lithium batteries
1) Battery capacity
The capacity of the battery is also called the battery's power, and the unit is Ah (Ah) or mAh (mAh). Ideal for a battery with a capacity of 1 Ah, it can be discharged for 1 hour with a current of 1 A when fully charged.
2) Charge/discharge rate
The charge/discharge rate indicates how much current is charged/discharged, and is generally calculated as a multiple of the nominal capacity of the battery, and is generally referred to as "how much C". For a 2500 mAh lithium battery, if the discharge rate is 1 C, the discharge current is 2500 mA, and the charge current is 0.2 C, which means the charge current is 500 mA.
3) Nominal voltage
The nominal voltage of a lithium battery is also called the rated voltage. The nominal voltage of an ordinary mobile phone battery is generally 3.7V. The voltage when the battery is fully charged is generally about 4.2V. The voltage when the battery is just discharged is generally about 2.5V.
4) Nominal power / nominal energy
According to the physics textbook, P=U*I, W=U*I*t, the unit of power is W (Watt), and the unit of energy is Wh (Watt). A battery with a capacity of 1500 mAh has a nominal voltage of 3.7V, a nominal power of 5.55W and a nominal energy of 5.55Wh.
5) Internal resistance
The battery can be equivalent to a voltage source with a voltage source with a certain internal resistance. For batteries, the smaller the internal resistance, the more expensive the internal resistance is.
The unit of internal resistance of the battery is Ω (ohm) or mΩ (milliohm). The internal resistance of the battery is mainly affected by the material and manufacturing process of the battery.
6) Cycle life
The cycle life of a battery generally refers to a cycle of filling and illuminating once. After the battery reaches the cycle life, the battery ages very much, and the battery capacity will drop a lot. The cycle life is also an important indicator for measuring the battery.
The IEC standard stipulates that the cycle life of the battery is maintained at 60% of the initial capacity after 500 cycles. The national standard stipulates that the capacity should be maintained at 70% of the initial capacity after 300 cycles.
7) Remaining power (SoC)
The remaining capacity of the battery refers to the percentage of the current battery power and the total available power, 0%~100%, reflecting how much power is still there. (SoC: State of Charge).
(2) Battery protection
Why do lithium batteries need protection?
Lithium batteries require a protection system due to their chemical activity, structure, etc. If there is no protection system, it may have a great impact on the service life of the battery. In severe cases, there may be a risk of explosion or combustion. Lithium batteries without a protective plate are forbidden.
Lithium batteries should be protected from deep charge, which will seriously affect the battery life. If you regularly add batteries to the battery, it will help the battery life. Many people need to use the mobile phone to automatically shut down before charging the mobile phone. This is a serious bad habit. One is that when the battery is low, the RF transmission power is large, the radiation is powerful, and the battery life is affected.
Friends who often use wireless charging, because the phone is placed on the wireless charger when not making a call, the wireless charger will recharge the phone in time, which is very helpful for the battery life.
Therefore, the best condition of the battery is not to overfill or overcharge.
The lithium battery protection system is as follows:
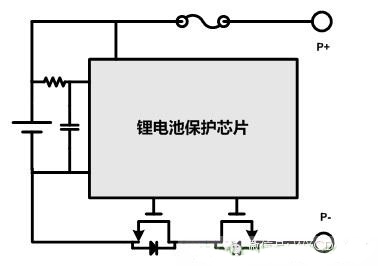
Lithium batteries require at least the following protective measures for their special reasons:
1) Overcharge protection
When the battery is almost full, the battery voltage generally reaches 4.2V, and the charging path needs to be cut off to prevent the battery from overcharging.
2) Over-discharge protection
When the battery is discharged quickly, the general battery voltage reaches about 2.5V (the voltage of different manufacturers will be different), and the discharge path needs to be cut off to prevent the battery from being over-discharged.
3) Over temperature protection
When the battery is charged or discharged or abnormal due to excessive current, the battery temperature will rise sharply. Generally, the battery temperature will reach 60~65°, and the charging and discharging circuit must be cut off to ensure the safety of the system.
Excessive battery temperature will have a great impact on the battery life. If the battery is operated in a high temperature environment for a long time, such as 45 ° or above, the battery life will be seriously shortened.
Many wireless charging receivers are close to the battery. Some manufacturers have unreasonable design of the receiving end, low efficiency, and severe heat generation. At the same time, it will seriously affect the battery life. Friends who do wireless charging must pay attention to this.
In addition, some protection systems protect the charging current and discharge current from overcurrent or short circuit.
The mobile phone battery has a protection system. If the battery is full, the battery protection system will automatically shut down, cut off the charging circuit, and do not worry about the danger of battery explosion.
(three) battery charging
Analyze the battery must analyze the battery charge, combined with wireless charging analysis. Lithium battery is also required for charging due to its own characteristics. If the battery is seriously over-discharged and the voltage is very low, the battery can only be charged with a small current, and the battery is slowly activated. Otherwise, the battery will be greatly damaged.
In addition, the high current and high rate of charging or discharging the battery are harmful to the battery, which will affect the service life of the battery.
In the industry, the charging process of the battery is generally divided into three sections: turbulence, constant current, and constant voltage.
When the battery voltage is too low, the first trickle charge is used. When the battery voltage is charged to the normal voltage, the constant current is quickly charged. When the battery is fully charged, it is turned into a small current and constant voltage charge to slowly replenish the battery.
for example:
Frequently, many friends sometimes want to simply compare the charging speed of two wireless chargers. Generally, two mobile phones have a low power (if 50%), and one has more power (if 90%). Minutes to see the results, a charge of about 5%, a charge of only about 1%, ask me how the difference is so big, I can only say that the difference between your comparison is too big.
In addition, what is full is judged by the battery voltage is not accurate, there is a standard in the industry, it is generally considered that the charging current is about 0.1 times of the constant current charging when the constant voltage charging is full.
The graph of the charging current and voltage of a lithium battery is as follows:
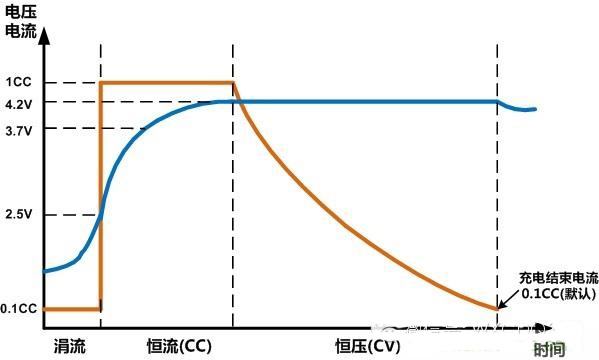
For the battery, the charging speed is mainly determined by the charging current in the constant current charging phase, which is not directly related to whether you use wired charging or wireless charging. Whether it is wired charging or wireless charging, as long as the charging current provided by the charger is large, the charging speed is fast.
resin encapsulated transformer,EI54 120v to 12v transformer,120v to 24v transformer,480v to 24v transformer
IHUA INDUSTRIES CO.,LTD. , https://www.ihua-transformer.com